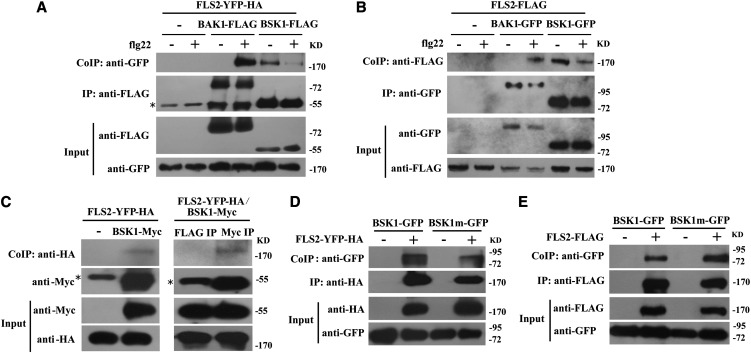
Figure 6.
BSK1 Forms a Protein Complex with FLS2.
(A) Co-IP of BSK1 and FLS2 from N. benthamiana transiently expressing BSK1-FLAG and FLS2-YFP-HA before (−) or 10 min after (+) elicitation with 1 μM flg22, as indicated. Total protein was extracted and subjected to immunoprecipitation of BSK1 protein by FLAG antibody, followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-GFP antibody. BAK1-FLAG was used an internal control. Asterisk indicates the heavy chain of IgG (∼55 kD).
(B) Co-IP of BSK1 and FLS2 from Arabidopsis protoplasts transiently expressing BSK1-GFP and FLS2-FLAG before (−) or 10 min after (+) elicitation with 1 μM flg22 as indicated. FLS2-FLAG alone was used as a negative control. The BSK1 protein was immunoprecipitated by GFP antibody, followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-FLAG antibody. BAK1-GFP was used as an internal control.
(C) Co-IP of BSK1 and FLS2 from transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Total protein was extracted from 3-week-old plants expressing both BSK1-Myc and FLS2-YFP-HA. Plants expressing FLS2-YFP-HA alone (left panel) or an immunoprecipitation with unrelated antibody (right panel) were used as negative controls. The BSK1 protein was immunoprecipitated by anti-Myc antibody, and the presence of FLS2-YFP-HA protein was detected by immunoblot analysis with anti-HA antibody.
(D) and (E) The bsk1-1 mutation did not affect BSK1 and FLS2 association in N. benthamiana or Arabidopsis protoplasts. Co-IP of BSK1 and FLS2 from N. benthamiana transiently expressing BSK1m-GFP (carrying the bsk1-1 mutation) and FLS2-YFP-HA (D) or Arabidopsis protoplasts transiently expressing BSK1m-GFP and FLS2-FLAG (E). BSK1-GFP or BSK1m-GFP alone was used as a negative control. Total protein was subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA (D) or anti-FLAG (E) antibody, followed by immunoblot analysis using anti-GFP antibody.
These experiments were repeated four times with similar results.