Figure 4.
Site-Directed Mutagenesis of cpTatC Identifies Regions Involved in Binding.
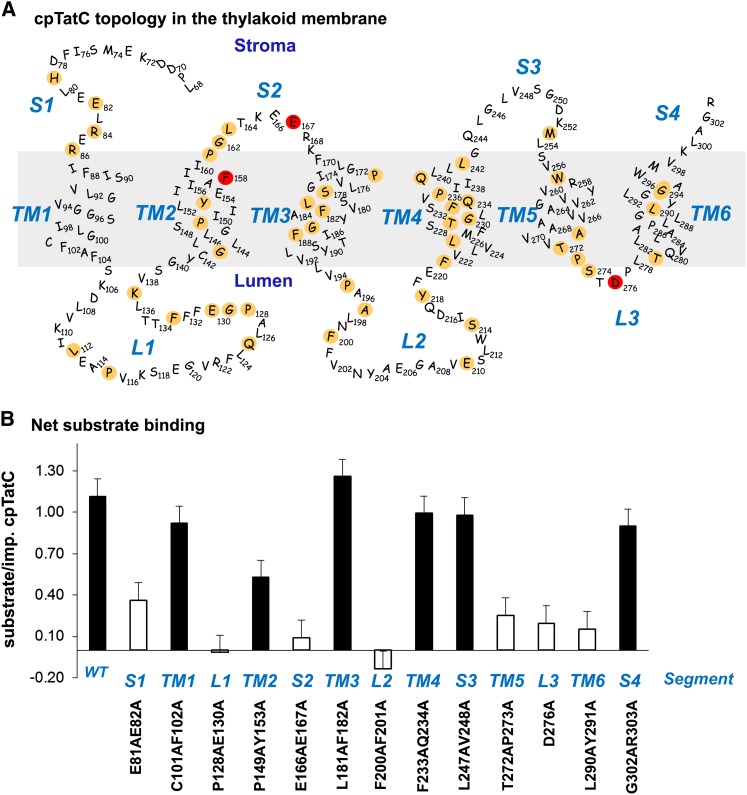
(A) Predicted structure and topology of the pea cpTatC protein. The nonconserved 67 residues of the N terminus are not shown. cpTatC is divided into stromal (S), transmembrane (TM), and lumenal (L) segments by topological location. Conserved residues identified by SIFT are colored tan. Residues Phe-158, Glu-167, and Asp-276, which correspond to the E. coli TatC essential residues Phe-94, Glu-103, and Asp-211, are colored red.
(B) Binding assays of the mutants in each segment of cpTatC. Wild-type (WT) and mutant precpTatC with Ala substitutions of pairs of conserved residues, as designated below the chart, were imported into chloroplasts. Recovered thylakoids were incubated with tOE17-20F for binding assays. The numbers of bound substrate per imported cpTatC are displayed as average + se (n = 3). Closed bars represent binding stoichiometry >40% of wild-type cpTatC; open bars represent ≤40% of the wild type.