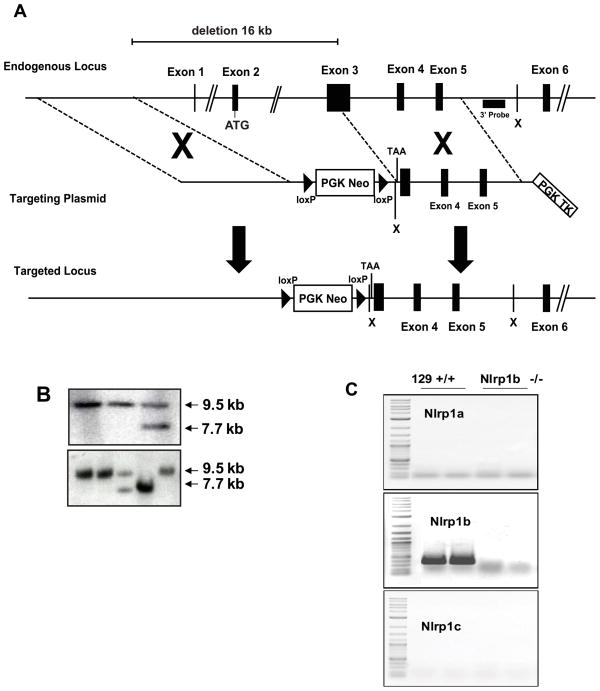
Figure 1. Generation of a Nlrp1 deficient mouse line.
(A) A schematic of the endogenous Nlrp1b locus, the targeting vector designed to disrupt the gene and the expected structure of the gene after homologous recombination. (B) Southern blot analysis of DNA from ES cells (upper panel) and from tail biopsies of pups generated from the intercross of mice carrying the modified Nlrp1b locus (lower panel) verified correct recombination of the plasmid with the endogenous locus and transmission of this allele through the germline. The expected 9.5kb XbaI fragment is observed in wild type ES cells and in mice carrying a wild type Nlrplb allele. Homologous recombination introduces a novel XbaI site reducing the size of the DNA fragment that binds to the probe to 7.7 kb. (C) RNA was prepared from the jejunum of 129 and Nlrp1b−/− mice and expression of all three Nlrp1 genes was examined by PCR using primers specific for each gene. As expected, 129S6 mice express only Nlrp1b, and this expression was not observed on analysis of RNA prepared from mice homozygous for the mutant allele.