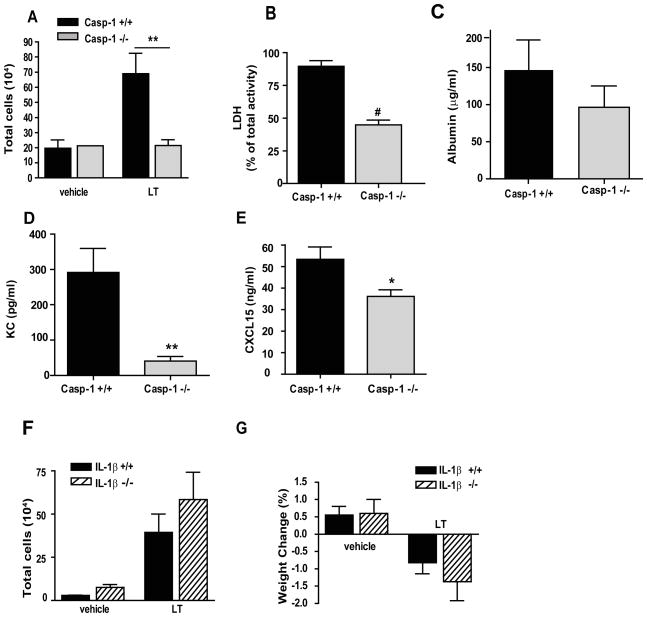
Figure 7. Lethal toxin-induced lung injury is dependent on caspase-1 but not IL-1β.
(A–E) Casp-1+/+ (black) and Casp-1 −/− (shade) mice were treated with PBS as a vehicle or 20 μg LT i.t. BAL fluid was collected at 72 h after treatment. (A) The total number of inflammatory cells collected in the BAL fluid. (B) Cell death in BAL fluid determined by LDH activity in supernatants and expressed as the percentage of total cellular LDH activity. (C) Vascular permeability evaluated as a concentration of albumin in the BAL fluid, measured by colorimetric assay. KC (D) and CXCL15/lungkine (E) in the BAL fluid were detected by ELISA. n = 2 mice per genotype for vehicle treatment and n = 10 mice per genotype for LT treatment. (F, G) Il1β+/+ (black) and Il1β−/−(striped) mice were treated as above. (F) The total number of inflammatory cells collected in BAL fluid. (G) The percentage of weight lost 72 h after treatment. n= 2 per genotype for vehicle treatment and n = 9 mice per genotype for LT treatment. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; # p < 0.0001.