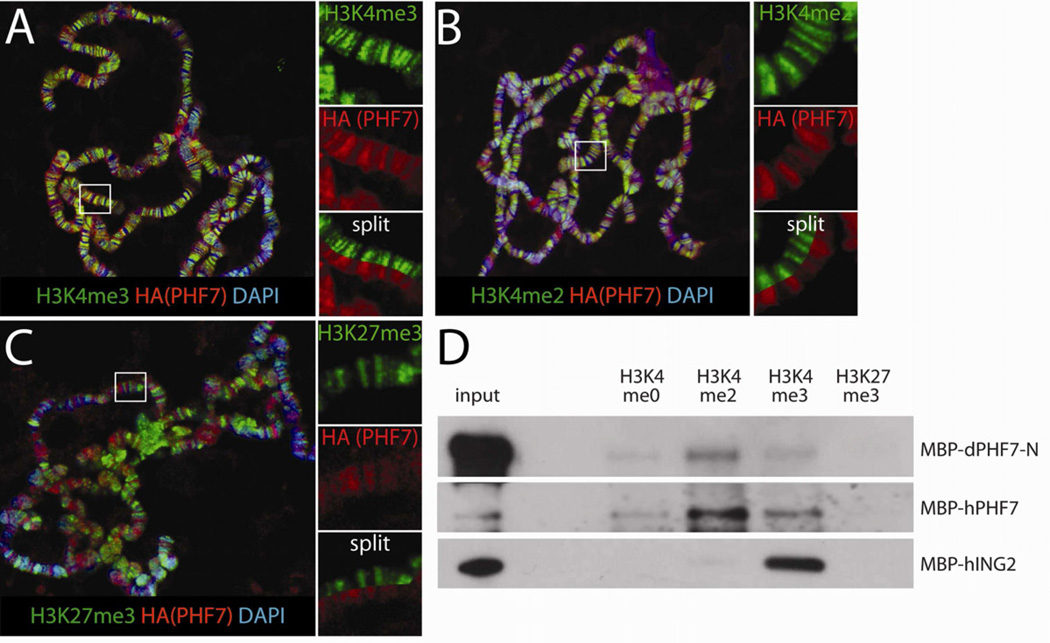
Figure 6.
PHF7 is a histone code reader. A–C) Polytene chromosomes isolated from salivary glands expressing UAS-Phf7-HA with fkh-Gal4 are co-labeled with antibodies for HA (PHF7) and various modifications on histone H3 tails as indicated. DAPI labels the DNA. A, H3K4me3. B, H3K4me2. C, H3K27me3. Smaller panels represent larger magnification of regions of the chromosomes (white rectangles) showing either the H3 mark (green) or HA-PHF7 (red) alone, or with the single channels split and aligned on the same image for direct comparison. D) α-MBP western blot analyses of MBP-tagged proteins precipitated with H3 N-terminal tail peptides modified as indicated. dPHF7-N is the N-terminal PHD finger domain of Drosophila PHF7, hPHF7 is full length human PHF7 and hING2 is the PHD finger of human ING2. Inputs are 1% for dPHF7 and hING2 and 10% for hPHF7. Note that the low specific activity of dPHF7-N in the binding assay was due to a tendency to aggregate in solution that was remarkably consistent with different protein fragments and purification conditions. See also Figure S5.