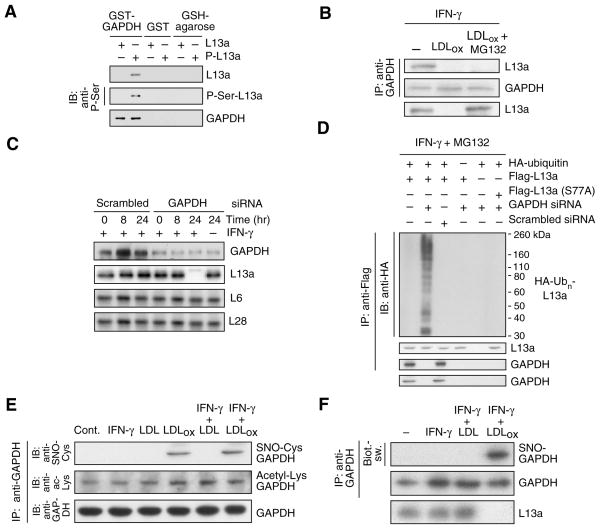
Figure 3. GAPDH binds phospho-L13a and protects it from degradation.
(A) GAPDH binds phospho-L13a in absence of other GAIT components. Unmodified and phosphorylated L13a (P-L13a, prepared by treatment with ZIPK) were incubated with GST-GAPDH or GST immobilized to glutathione (GSH)-agarose beads. After washing, binding was detected by immunoblot analysis with anti-L13a, -phospho-Ser and -GAPDH antibodies.
(B) LDLox blocks GAPDH binding to phospho-L13a. Cells were treated with IFN-γ, LDLox, and MG132 as shown. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GAPDH antibody, and immunoblotted with anti-L13a and -GAPDH antibodies. Total L13a was detected by immunoblot with anti-L13a antibody.
(C) GAPDH protects L13a from degradation. U937 cells were transfected with GAPDH (or scrambled) siRNA. After recovery, cells were treated with IFN-γ, and lysates immunoblotted with anti-GAPDH, -L13a, -L6, and -L28 antibodies.
(D) GAPDH prevents ubiquitinylation of phospho-L13a in cells. U937 cells were co-transfected with GAPDH (or scrambled) siRNA and with plasmids encoding HA-ubiquitin and Flag-tagged L13a (wild-type or S77A mutant). After recovery, cells were incubated with IFN-γ and MG132 for 24 hr. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, and immunoblotted with anti-HA, -L13a, and -GAPDH antibodies. Total GAPDH was determined by immunoblot with anti-GAPDH antibody.
(E) LDLox induces S-nitrosylation of GAPDH. Cells were treated with IFN-γ, LDL, and LDLox. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GAPDH antibody and immunoblotted with anti-GAPDH, -S-nitrosocysteine (SNO-Cys), and -acetyl-Lys antibodies.
(F) Determination of GAPDH S-nitrosylation by biotin-switch assay. S-nitrosylation of endogenous GAPDH and L13a degradation were determined in human PBM treated with IFN-γ in presence of LDL or LDLox for 24 hr. GAPDH was immunoprecipitated and S-nitrosylation detected with avidin-HRP in the biotin-switch assay. Efficiency of immunoprecipitation was shown by immunoblot analysis with anti-GAPDH antibody.