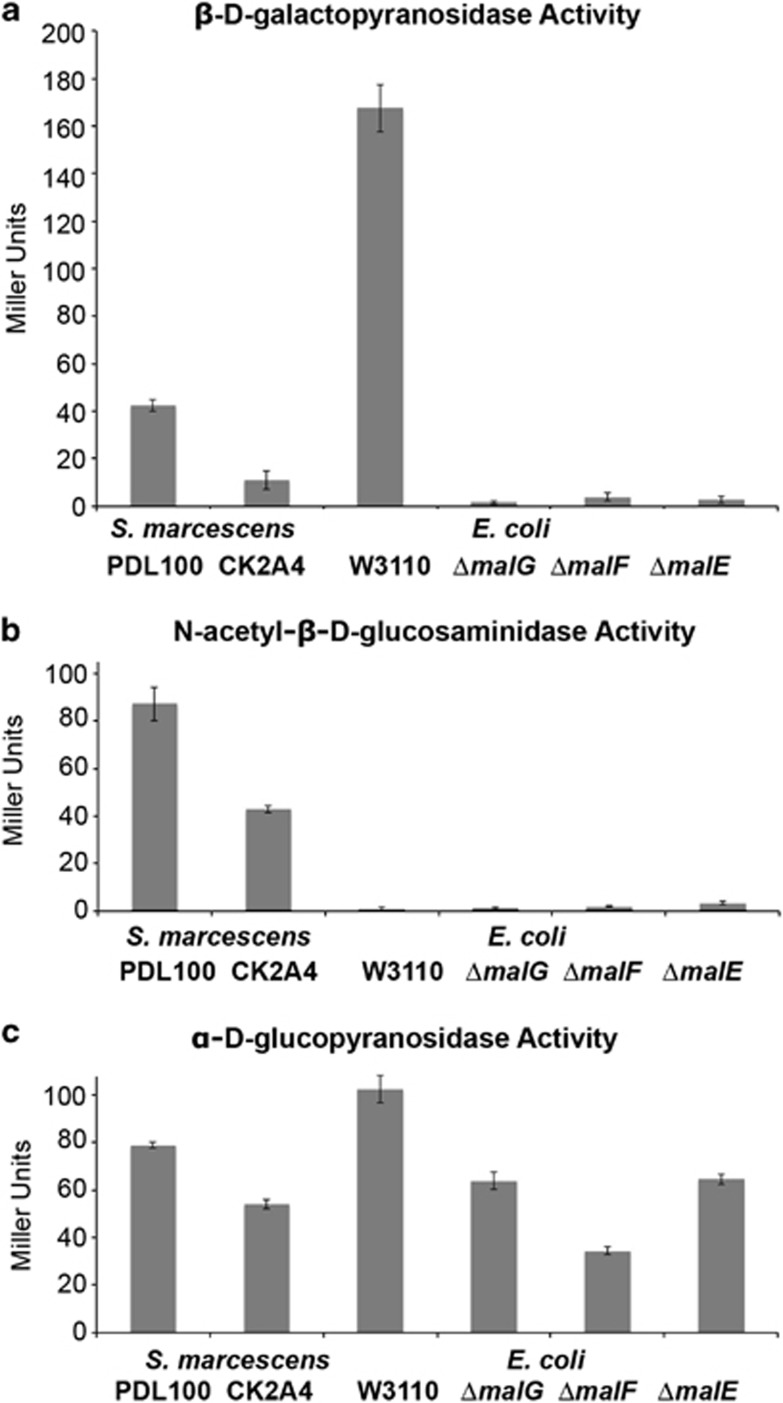
Figure 1.
Enzymatic activities in mutants of S. marcescens and E. coli. Overnight cultures of wild-type S. marcescens PDL100 and the transposon mutant (CK2A4) were tested for activities of (a) β-𝒟-galactopyranosidsase, (b) N-acetyl-β-𝒟-glucosaminidase and (c) α-𝒟-glucopyranosidase using a Miller assay (Miller, 1972) with appropriate p-nitrophenyl-glycoside substrates. E. coli W3110 and individual in-frame single gene knockouts of malE, malF and malG were also tested to compare phenotypes of CK2A4 with those of the defined well-characterized E. coli mutants in the malEFG operon. All cultures were grown overnight before the assays; S. marcescens was cultured in Marine broth, E. coli was grown in LB. Averages of three biological and four technical replications are shown. Error bars are standard error. There was a significant reduction in the enzymatic activities between wild-type S. marcescens and CK2A4 (β-𝒟-galactopyranosidsase: t=13.55, dF=6, P<0.0001; N-acetyl-β-𝒟-glucosaminidase: t=12.22, dF=3.3, P=0.0008; α-𝒟-glucopyranosidase: t=20.86, dF=4.87, P<0.0001). In E. coli, β-𝒟-galactopyranosidsase and α-𝒟-glucopyranosidase activities were reduced in malE, malF and malG mutants.