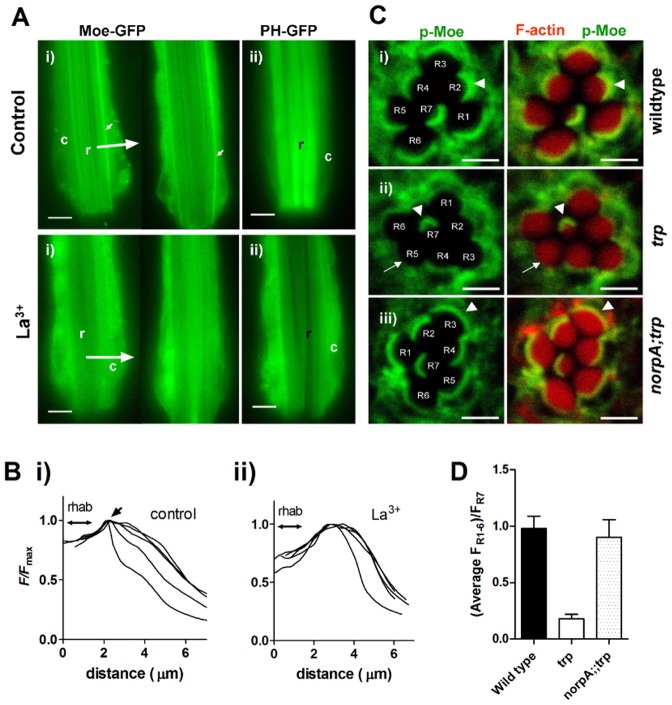
Fig. 7.
Depletion of dMoesin from rhabdomere bases following red light exposure in the absence of TRP channels. (A) (i) Dissociated live ommatidia (∼2/3 of ommatidial length imaged, distal ends downwards) expressing GFP-tagged Moesin after continuous red illumination for 3–20 min in control bath (top row) and in the presence of 100 µM La3+, which phenocopies the trp mutation by blocking all TRP channels (bottom row). Note the prominent stripes of fluorescence at the base of the rhabdomeres (small arrows), which are no longer seen after red illumination in the presence of La3+ (two examples shown; representative of 18 control and 24 La3+-treated ommatidia). (ii) Ommatidia expressing the PtdIns(4,5)P2-binding PH domain from PLCδ1 (PH–GFP). In control solutions PH–GFP remained localized to the rhabdomeres (r) after red illumination; but in La3+-treated ommatidia (below) it had translocated to the cell body (c), indicating severe depletion of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in the rhabdomeres (representative of 4–7 ommatidia in each condition). See also supplementary material Movies 1 and 2. Scale bars: 5 µm. (B) Representative intensity profiles (averaged line scans from rhabdomere to periphery at 90° to rhabdomere long axis, as indicated by large arrows in A from five control ommatidia (i) and five ommatidia exposed to La3+ (ii); a sharp peak representing the stripe of Moesin (arrow) adjacent to the rhabdomere (indicated by double arrow) is only apparent in control. (C) Transverse confocal slices of ommatidia from fixed whole-mount preparations of eyes exposed to red light for 2 hours. The retinae were probed with anti p-Moe (green), and Rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin (red), which labels actin in the rhabdomeres. Left: p-Moe alone; right: merged images. (i) In the wild-type retina, p-Moe is concentrated in a band at the base of the rhabdomeres (white arrowhead). (ii) In the trp343 retina, the white arrow indicates the absence of p-Moe from the bases of rhabdomeres R1–R6 . R7, which does not respond to red light retains the band at the base (white arrowhead). (iii) Localization of p-Moe to the base of the rhabdomeres was rescued in norpAP24;;trp343 double mutants. Scale bars: ∼2 µm. (D) Quantification of the fluorescence intensity in the basal band of p-Moe immunofluorescence in R1–R6 normalised to that in R7, which served as an internal standard (means ± s.e.m. of nine ommatidia from three flies).