Table 2.
Ranitidine population parameter estimates from the BASE and FINAL models developed from the original data set of 78 patients, and mean parameter estimates from the FINAL model fitted to the bootstrap and jack-knifed samples
| Parameter | Original data set (n = 184) | 1000 Bootstrap samples | Jack-knifed samples | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BASE model | FINAL model | Bootstrap | Jack-knife | |||||||
| Estimate | RSE% | Estimate | RSE% | Mean | RSE% | %Diff | Mean | RSE% | %Diff | |
| CL (l h−1) | ||||||||||
| θCL | 32.4 | 25.8 | 32.1 | 27.4 | 33.3 | 25.2 | 3.9% | 32.1 | 25.7 | 0.1% |
| V (l) | ||||||||||
| θV | 275 | 25.7 | 285 | 34.3 | 309.7 | 45.8 | 8.7% | 285.4 | 41.7 | 0.1% |
| ka (h−1) | ||||||||||
| θka | 0.429 | 23.5 | 1.31 | 26.1 | 1.305 | 52.6 | −0.4% | 1.309 | 36.2 | −0.1% |
| F1 | ||||||||||
| θF1 | 0.349 | 26.9 | 0.275 | 27.1 | 0.296 | 25.7 | 7.6% | 0.275 | 28.8 | 0.0% |
| θ(HEART,CL) | — | — | 0.463 | 23.5 | 0.485 | 23.6 | 4.8% | 0.463 | 25.4 | 0.0% |
| IIVCL (CV%) | ||||||||||
| ωCL | 70.1 | 28.5 | 60.1 | 33.0 | 57.8 | 19.6 | −3.8% | 60.0 | 20.4 | −0.2% |
| IIVV (CV%) | ||||||||||
| ωV | 86.3 | 58.1 | 85.0 | 44.5 | 83.8 | 31.5 | −1.4% | 85.0 | 24.6 | 0.0% |
| Residual (CV%) | ||||||||||
| σprop | 60.0 | 12.6 | 59.5 | 13.4 | 59.1 | 6.9 | −0.7% | 59.5 | 7.2 | 0.0% |
The BASE model includes weight as a covariate on clearance and volume, as follows:
Final model: 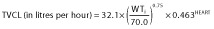 and
and 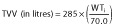
Definitions are as follows: IIVCL is the interindividual variability in clearance (CL); IIVV is the interindividual variability in the volume of distribution (V); σprop is the residual variability (proportional error model); RSE% is the percentage relative standard error of parameter estimates; and coefficient of variation (CV)% is the percentage coefficient of variation.
Percentage difference 
