Figure 2. Neutrophil egression from the bone marrow does not depend on CXCR2 signaling during sepsis.
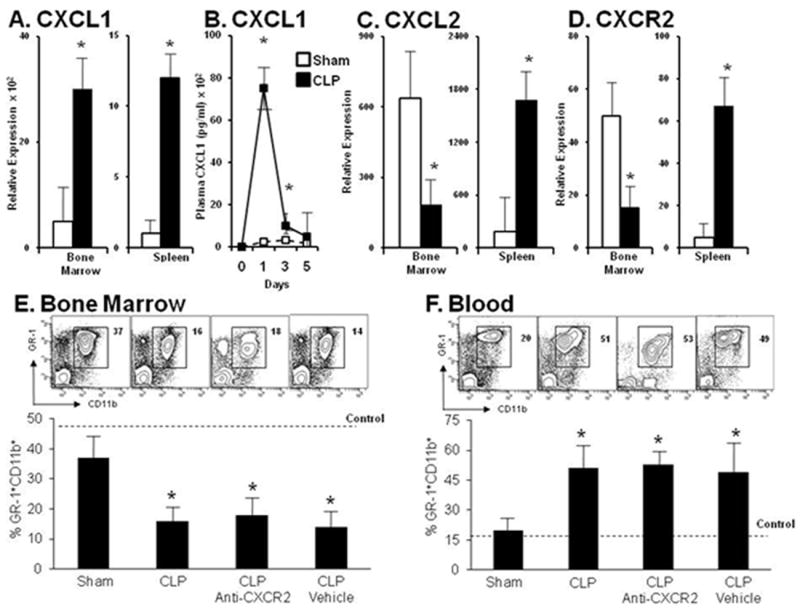
Panel A. Relative transcription level of CXCL1 in the bone marrow and spleen at 12 hours after the induction of sepsis. Panel B. Blood plasma elevation of CXCL1 levels extends through day 5 compared with sham levels. Panel C. Relative transcriptional level of CXCL2 in the bone marrow and spleen in sham and CLP treated mice12 hours after sepsis. Panels D. Relative transcriptional level of CXCR2 in the bone marrow and spleen of sham and CLP treated mice 12 hours after sepsis. Panel E. Depicts representative contour plots and bar graphs of GR-1+CD11b+ levels in the bone marrow of mice receiving CXCR2 blockade or vehicle control in sham and CLP treated animals. Panel F. Depicts representative contour plots and bar graphs of GR-1+CD11b+ levels in the blood of mice receiving CXCR2 blockade or vehicle control in sham and CLP treated animals. Values for panels A-D represent the mean and standard error of 5-7 animals per group from two independent experiments. Values for panels E and F represent the mean and standard error of 5 animals per group from three independent experiments. A, C, D, E and F * p<0.01 by Student’s t-test between sham and CLP groups. B *p<0.05 by analysis of variance and a post hoc Dunn’s test of significance at each time point compared to time point 0.
