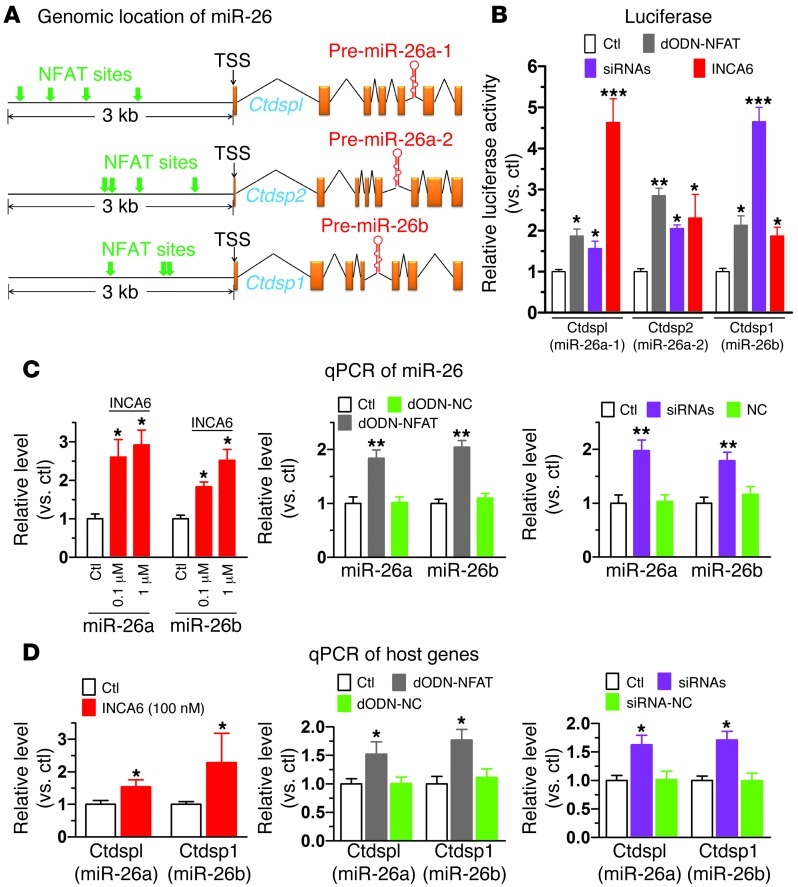
Figure 6. Transcriptional regulation of miR-26 by NFAT.
(A) Schematic genomic maps of the 3 miR-26 family members showing human host genes, intronic locations of pre–miR-26a/b, and putative NFAT binding sites (indicated by arrows) in the 5′ flanking regions. (B) Effects of NFAT inhibition on promoter activities of the host genes of human miR-26 family members: Ctdspl/miR-26a-1, Ctdsp2/miR-26a-2, and Ctdsp1/miR-26b, determined by luciferase activity assay using pGL3 vector carrying the promoter regions containing NFAT-binding sites. NFAT was inhibited by INCA6 (100 nM), sequestered by dODN (dODN-NFAT; 10 nM), or silenced by siRNAs to NFATc3 and NFATc4 (10 nM). Negative controls failed to affect luciferase activity (data not shown). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control; n = 4/group. (C) Effects of NFAT inhibition by INCA6 (left panel; n = 5/group), dODN-NFAT (10 nM; middle panel; n = 6/group), and siRNA (10 nM; right panel; n = 6/group) on miR-26a and miR-26b levels, determined by qPCR in H9c2 cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control. (D) Effects of NFAT inhibition on expression of miR-26 host genes, determined by qPCR in H9c2 cells. Note that NFAT inhibition does not affect miR-1 levels (Supplemental Figure 13). *P < 0.05 vs. control; n = 6/group. Values are mean ± SEM.