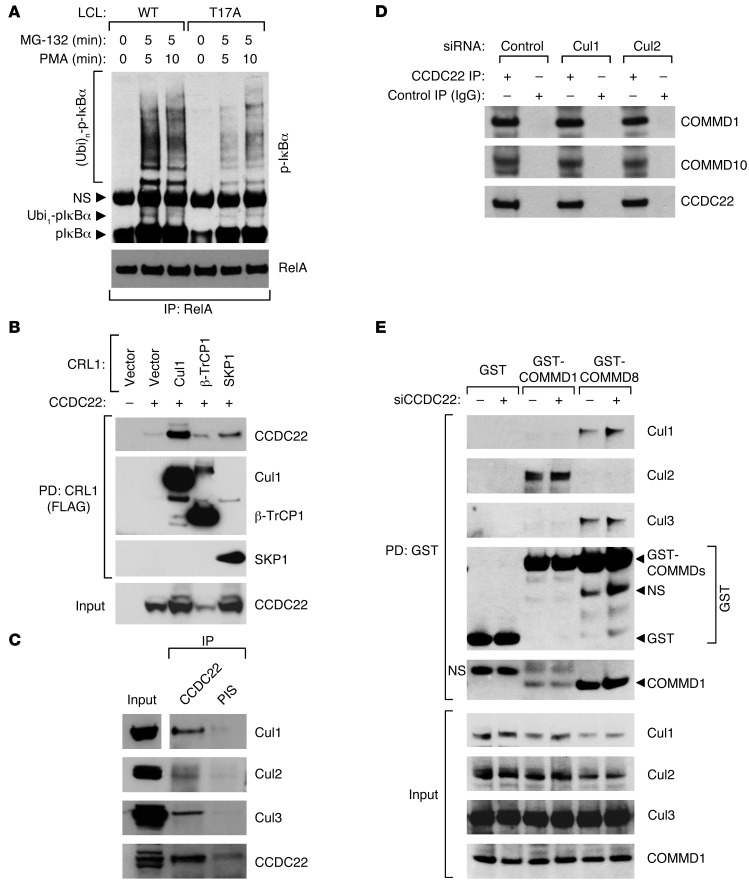
Figure 6. CCDC22 is required for IκB ubiquitination.
(A) IκB-α ubiquitination is reduced in lymphoid cells bearing the T17A mutation. LCLs derived from a healthy control subject and an XLID patient with the T17A mutation were stimulated with PMA. The protease inhibitor MG-132 was concurrently administered. Ubiquitinated phospho–IκB-α levels were determined by immunoprecipitating NF-κB complexes with a RelA antibody, followed by phospho–IκB-α immunoblotting. (B) CCDC22 interacted with various CRL1-βTrCP components. FLAG-tagged Cul1, βTrCP1, or SKP1 were expressed along with CCDC22 in HEK 293 cells. CRL components were immunoprecipitated using a FLAG antibody, and CCDC22 was detected in the recovered material by immunoblotting. (C) Endogenous CCDC22 interacted with Cul1, Cul2, and Cul3. CCDC22 was immunoprecipitated, and the recovered material was immunoblotted for endogenous Cul1, Cul2, and Cul3. Some input lanes corresponded to different exposures of the same film. (D) Cul1 and Cul2 were not required for CCDC22-COMMD interaction. HEK 293 cells were treated with siRNA against Cul1, Cul2, or an irrelevant control. Endogenous CCDC22 was subsequently immunoprecipitated, and the recovered material was immunoblotted for endogenous COMMD1 and COMMD10. (E) CCDC22 was not required for Cullin-COMMD interaction. HEK 293 cells were transfected with GST, GST-COMMD1, or GST-COMMD8 along with control or anti-CCDC22 siRNA. After 48 hours, cell lysates were purified on GST-agarose, and the recovered material was immunoblotted for endogenous Cul1, Cul2, Cul3, and COMMD1.