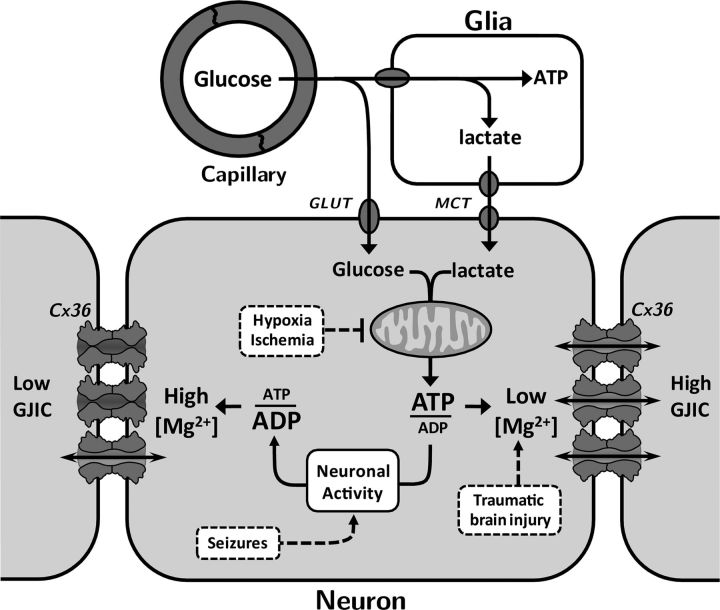
Figure 11.
Diagram illustrating relation between ATP/ADP ratio and [Mg2+]i and the effect on Cx36 GJ channels. During sleep and reduced neuronal activity, ATP/ADP ratio is increased by mitochondrial metabolism of glucose and lactate coming from capillaries and surrounding glia, respectively. During wake period and enhanced neuronal activity, ATP/ADP ratio is decreased. Changes in ATP have a direct effect on [Mg2+]i, leading to changes in Cx36-dependent GJIC. Pathological conditions, such as hypoxia, ischemia, and seizures may result in decreased GJIC, while traumatic brain injury may lead to increased GJIC. GLUT, glucose transporter; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter.