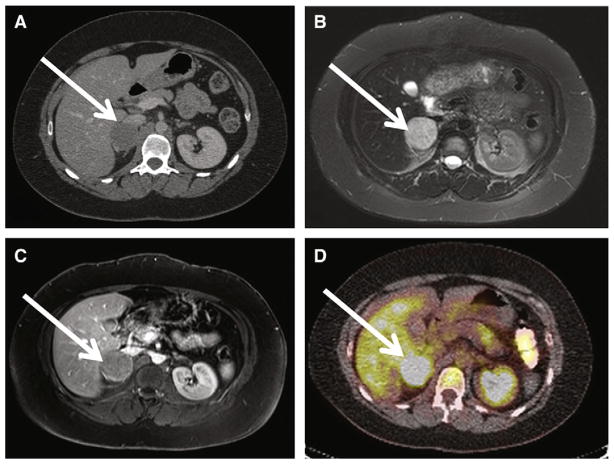
Fig. 4.
Shown is a 30-year old woman with history of hypertension and headache and sporadic adrenal PGL/pheochromocytoma. A, Axial contrast CT at the level of the right adrenal gland demonstrates a heterogeneously enhancing 4 × 4 × 5-cm mass consistent with right adrenal PGL/pheochromocytoma (white arrow). Portal venous phase CT attenuation of this mass was 65 HU. B, Axial T2-weighted image demonstrates homogenous T2 hyperintensity of patient’s right adrenal PGL. T2 signal is hypointense to CSF, but hyperintense to liver and spleen (group 2 classification according to criteria proposed by Jacques et al13). C, axial postcontrast MRIs demonstrate enhancing right adrenal PGL (white arrow). D, 18F-FDG-PET CT images demonstrate hypermetabolic focus corresponding to patient’s right adrenal PGL with maximal SUV of 6. The patient underwent right laparoscopic adrenalectomy, confirming right adrenal PGL/pheochromocytoma.