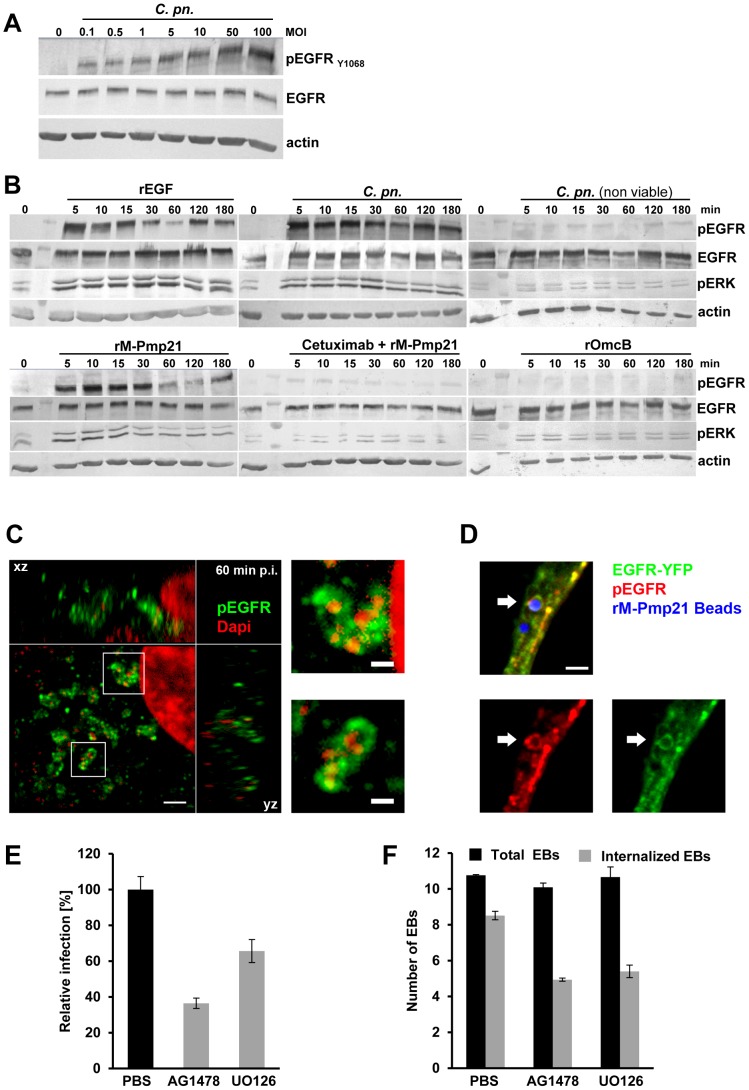
Figure 5. EGFR signaling is activated by C. pneumoniae EBs and recombinant Pmp21.
(A) Kinetics of C. pneumoniae EB-induced phosphorylation of EGFR. HEp-2 cells were left uninfected (0) or infected with increasing numbers of C. pneumoniae EBs (MOI) for 60 min. The immunoblots show total levels of EGFR (EGFR) and levels of activated receptor (pEGFR, phosphorylated at Tyr1068) detected as described in Experimental Procedures. (B) Time courses of EGFR activation by rEGF (100 ng/ml), purified (viable and non-viable) C. pn. EBs (MOI 5), rM-Pmp21 (100 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of Cetuximab (5 µg/ml), and rOmcB (100 µg/ml). HEp-2 cells were serum-starved for 12 h at 37°C, shifted to 4°C for 10 min before the addition of bacteria or recombinant proteins, then incubated further at 37°C. The immunoblots show overall levels of EGFR (EGFR), activated EGFR (pEGFR) and activated ERK (pERK), the downstream MAP kinase. Actin served as loading control. (C–D) Confocal spinning-disk microscopy of C. pneumoniae EBs (C) or rM-Pmp21-coated latex beads (D) surrounded by ring-like structures of activated EGFR (pEGFRY1068). Scale bars 1 µm. (C) HEp-2 cells were infected with C. pneumoniae for 60 min. Two examples of internalized EBs surrounded by EGFR (white boxes) are shown at a higher magnification on the right. (D) Beads coated with rM-Pmp21 were added to EGFR-YFP-expressing CHO-K1 cells and incubated for 4 h at 37°C. The arrow marks a bead in the focal plane harboring EGFR and pEGFR rings. (E) EGFR inhibitors reduce infection by C. pneumoniae EBs. Confluent HEp-2 cells were pretreated for 2 h with PBS, AG1478 or UO126, and infected with C. pneumoniae EBs (MOI 1) for 48 h. The data represent the means of four independent experiments. (F) Internalization of C. pneumoniae EBs (MOI 1) by HEp-2 cells treated for 2 h with PBS, AG1478 or UO126. Internalized EBs were quantified as described in Experimental Procedures. The data represent the means of five independent experiments.