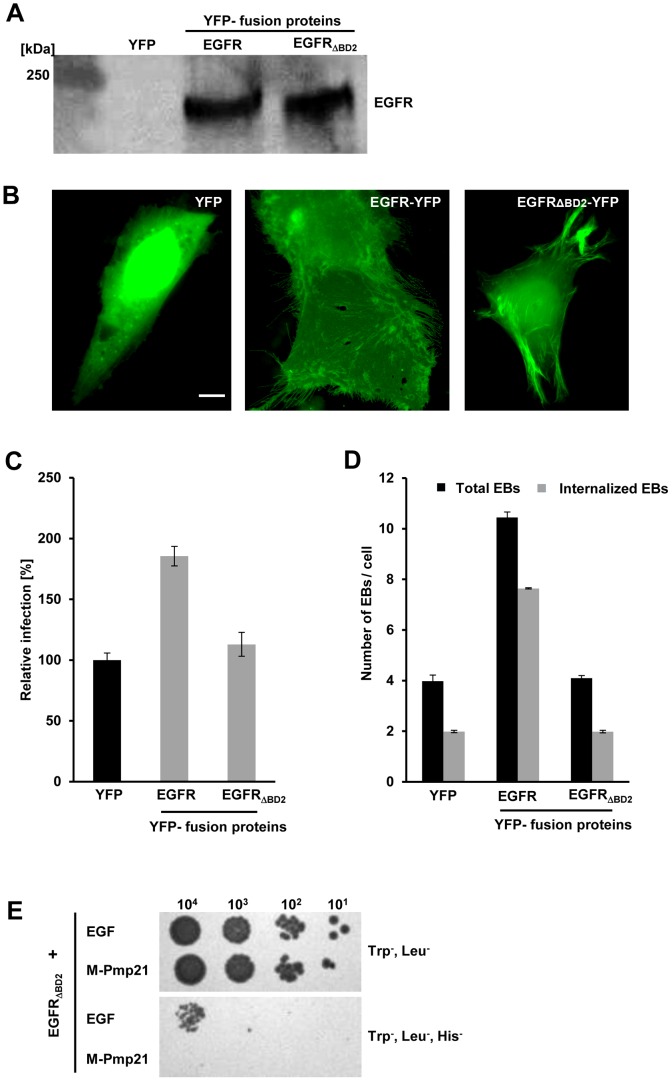
Figure 6. A functional EGF-binding domain in EGFR is essential for infection by C. pneumoniae.
(A–D) EGFR-deficient CHO-K1 cells were transfected with EGFR-YFP, EGFRΔBD2-YFP or YFP alone for 24 h. (A) EGFR expression was quantified by immunoblot analysis of lysates of transfected cells using an anti-EGFR antibody. (B) Subcellular localization of YFP and the two EGFR-YFP constructs by direct immunofluorescence of transfected CHO-K1 cells. Bar 5 µm. (C) Susceptibility of transfected CHO-K1 cells to infection with C. pneumoniae GiD. Cells were incubated with EBs (MOI 1) for 48 h. Inclusions were quantified using an antibody directed against the inclusion membrane protein Cpn0147. The data represent the means of four independent experiments. (D) Internalization of C. pneumoniae EBs (MOI 1) by CHO-K1 cells transfected with YFP, EGFR-YFP or EGFRΔBD2-YFP. Numbers of internalized EBs were determined in positively transfected cells only. The data represent the means of five independent experiments. (E) Y2H analysis of EGFRΔBD2/EGF and EGFRΔBD2/M-Pmp21 interactions. Serial dilution patch test of 101–104 cells on selective medium.