Figure 3. Similar early inflammation following pulmonary challenge with WT and yopK Y. pestis is resolved in the absence of YopK.
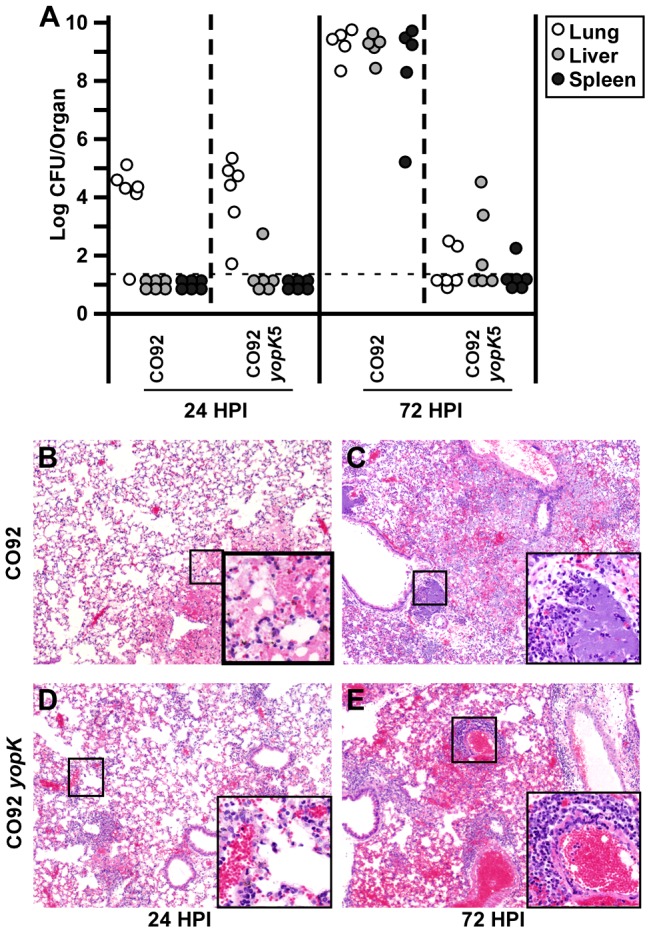
BALB/c mice were challenged by intranasal infection with 1×104 CFU of WT Y. pestis CO92 or 1×106 CFU of CO92 yopK. At 6, 24 and 72 HPI, mice were euthanized and lungs, livers, and spleens were divided with one-half tissue analyzed for bacterial titers (A) including lungs (open), liver (grey) and spleen (black) and the second half formalin fixed, sectioned and stained for histochemistry (B–E). H&E stains of WT-infected lungs (B–C) and yopK-infected lungs (D–E) from 24 (B,D) and 72 (C,E) HPI. Data shown were collected in two independent experiments, n = 6 mice per time point per strain. Statistical significance of differences in bacterial titer of WT- and yopK- infected lungs was analyzed by unpaired Student's t-test, *p<0.05. (B–E) Boxes show 4× magnified section of indicated area.
