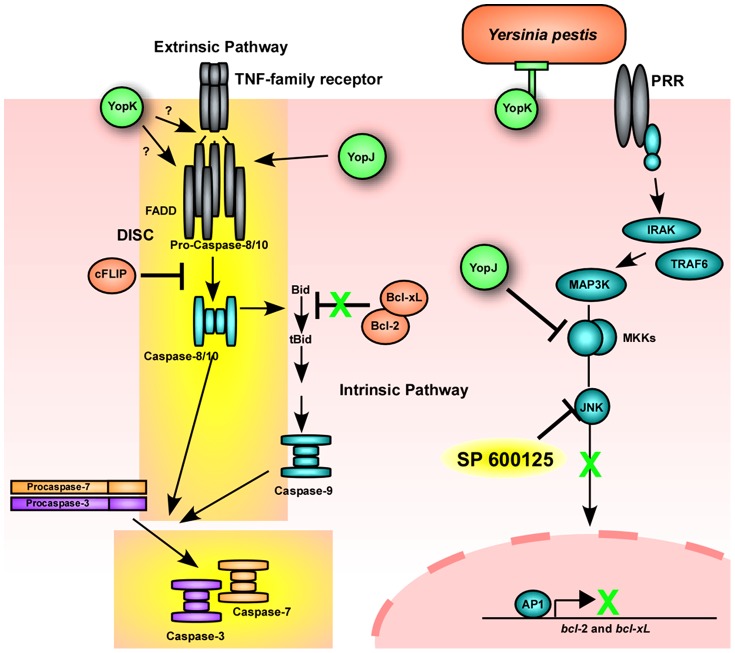
Figure 9. A model for Yersinia pestis induced apoptosis of macrophages.
Infection of RAW macrophages induces caspase-3-apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway by manipulating host signaling through type III secretion system effectors YopJ and YopK. YopK is located at the plasma membrane where it may control injection of effector Yops but may also be required to induce formation of the DISC death receptor complex, composed of pro-caspase-8 and -10, FADD and cFLIP, which is necessary for activation of caspase-8. In the absence of DISC complex formation, small amounts of active caspase-8 can cleave Bid to tBid in the absence of anti-apoptotic factors whose expression is repressed through the action of YopJ (green X). Formation of the DISC complex is regulated by YopJ. The small molecule SP600125 inhibits JNK phosphorylation, thereby causing reduced production of anti-apoptotic genes. Yellow background denotes the signaling pathway that may be specific to RAW cells and perhaps other immune cells.