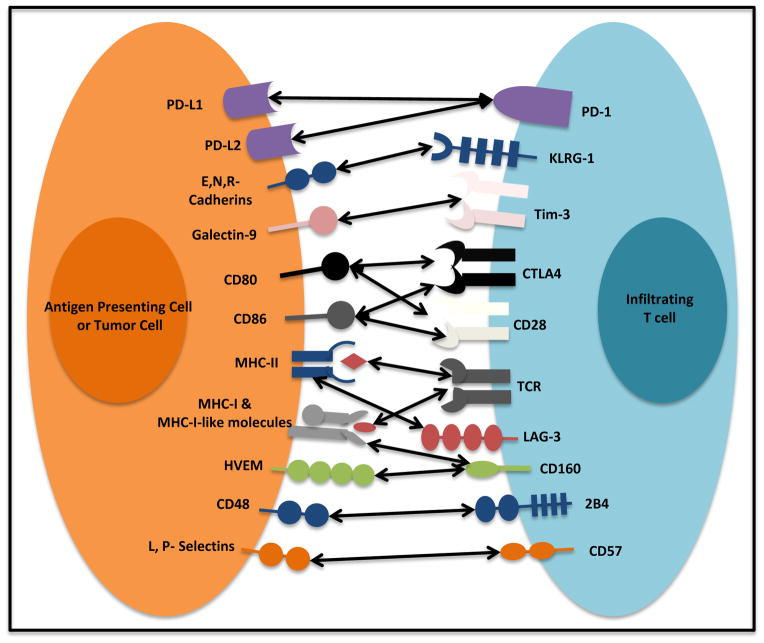
Figure 2. Immunoregulatory receptors and their ligands.
T cell activation relies on the T cell receptor (TCR) recognizing its cognate antigen in the context of MHC molecules from an antigen presenting cell (APC) or an APC-like cell (tumor cell). Interaction between co-stimulatory molecules CD80, and CD86 and CD28 is crucial for appropriate T cell activation. Immunoregulatory receptors such as CTLA-4 and PD-1 are to fine tune T cell activation. High levels of multiple immunoregulatory receptors (LAG-3, 2B4, CD160, KLRG1, Tim-3, CTLA-4, and CD57) or their ligands are found in the tumor microenvironment. Potent and lasting immunoregulatory signaling results in reduced T cell function and tolerance.