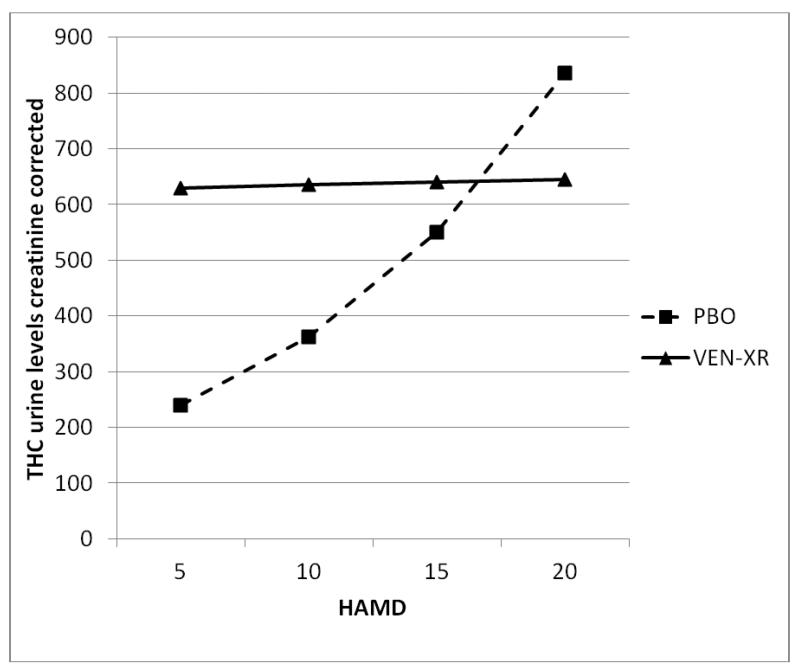
Figure 3.
Modeled THC urine levels creatinine corrected based on the treatment assignment (VEN-XR, n=51; PBO, n=52) and HAMD score.
* When analyzed longitudinally, THC urine levels creatinine corrected were associated with HAMD score but the interaction between week and HAMD score was not significant (F6,354=0.96, p-value=0.45) so it was omitted from the final model. Additionally, week as a main effect was not significant (F6,354=0.96, p-value=0.45) and thus was omitted suggesting that the effect of HAMD on the THC urine levels is the same throughout the study.
** For each treatment group, THC urine levels were differently associated with HAMD score, demonstrated by significant interaction between HAMD and treatment (see Table 2).
*** When the groups were analyzed separately, in the VEN-XR group there was not a significant relationship between HAMD score and THC urine levels creatinine corrected (see Table 2). However, for the PBO group, THC was associated with HAMD score (see Table 2).