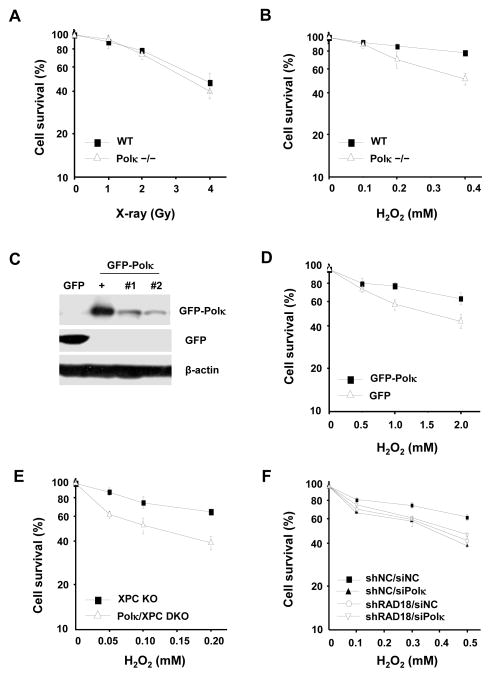
Figure 6.
The sensitivity of Polκ-deficient MEFs to DNA damage agent H2O2. Polκ−/− MEFs were treated with X-rays (A) or H2O2 at 4°C for 1 h (B) and further incubated in fresh medium for 7–10 days. (C) Cell lysates of Polκ−/− MEFs complemented with GFPor GFP-Polκ were separated by SDS-PAGE and then incubated with anti-GFP or anti-β-actin antibodies. “+” represents a positive control. “#1”and “#2” are two different stable clones. (D) Polκ−/− MEFs complemented with GFP or GFP-Polκ were treated with H2O2 at 4°C for 1 h and further incubated in fresh medium for 7–10 days. (E) Polκ and XPC double knockout MEFs were treated with H2O2 as in (D). (F) Polκ in Rad18-depleted U2OS cells was transiently knocked down and the sensitivity of the cells to H2O2 treatment were examined as in (D). Surviving fraction was expressed as a percentage of mock-treated cells. Values are the mean of three independent experiments (+/− SE).