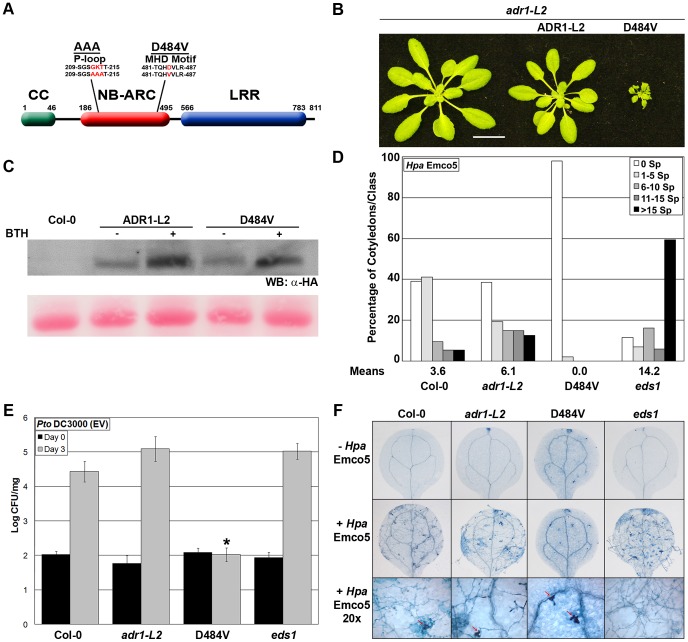
Figure 4. ADR1-L2D484V ectopically activates basal defense.
(A) Schematic representation of ADR1-L2 showing the P-loop and MHD mutations used in this study. (B) Morphology of five-week-old adr1-L2, and adr1-L2 complemented with pADR1-L2::ADR1-L2-HA or pADR1-L2::ADR1-L2D484V-HA, showing relative size. White bar is 2 cm. (C) Western blot of HA-tagged protein from the indicated genotypes before and after BTH application. Protein was extracted from plants, run on a denaturing gel and probed with anti-HA antibody. Ponceau-stained blot shows relative loading. (D) Ten-day-old seedlings were inoculated with 5×104 sporangia/mL Hpa Emco5 via spray inoculation. Sporangiophores per cotyledon were counted 4 dpi, with an average of 80 cotyledons per genotype counted. Sporangiophore counts were classified into: no sporulation (0 sporangiophores/cotyledon), light sporulation (1–5), medium sporulation (6–10), heavy sporulation (11–15), or very heavy sporulation (>15). Means of sporangiophore per cotyledon are listed below the graph. (E) Twenty-day-old seedlings were dip-inoculated with Pto DC3000(EV). Bacterial growth was assayed at 0 and 3 dpi. Values are mean cfu/mg ±2× SE, n = 4. Asterisk indicates significant difference (Post Hoc test, p<0.0001). (F) Trypan blue stained leaves from (D) and magnified sites (20×). Leaves were collected and stained 4 dpi. Red arrows indicate HR sites.