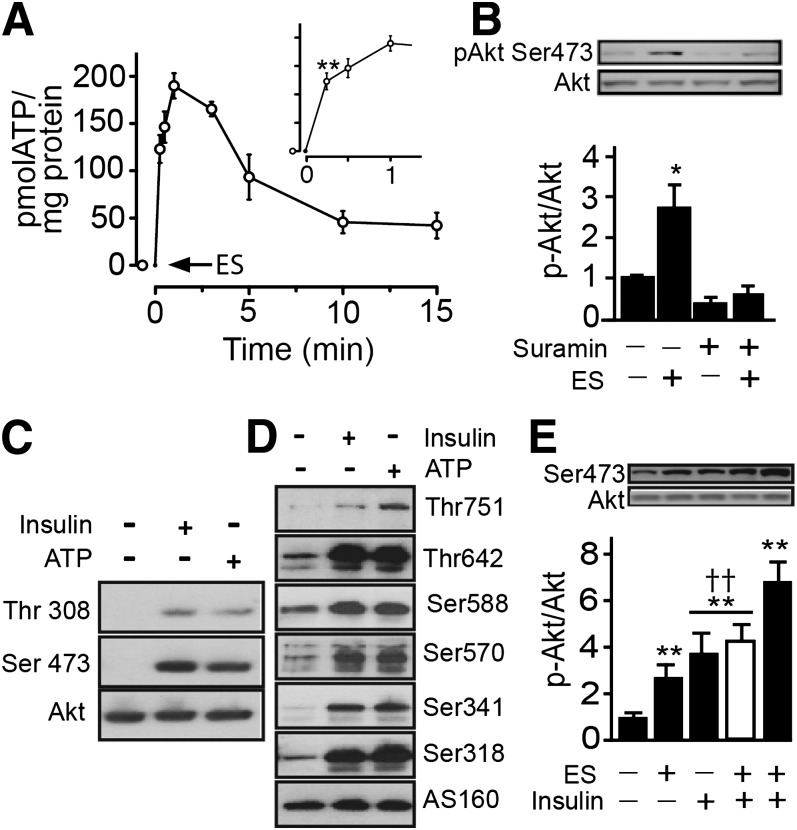
FIG. 2.
Electrical stimulation (ES) induces ATP-dependent Akt-AS160 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle cells. A: Primary myotubes were electrically stimulated, then aliquots of the extracellular medium were removed at the indicated times. ATP was measured by the luciferin/luciferase assay and quantified against a standard curve, as indicated in research design and methods. Cell lysates were analyzed for pAkt, total Akt, pAS160, and total AS160. B: Primary myotubes were preincubated for 30 min, with or without suramin (100 μmol/L), followed by assay of Akt phosphorylation at Ser473. C: L6-GLUT4myc-AS160 muscle cells were stimulated with exogenous ATP (100 μmol/L) or insulin (100 nmol/L) for 5 min, and then Akt phosphorylation at Thr308 and Ser473 was measured. D: L6-GLUT4myc-AS160 myoblasts were stimulated with exogenous ATP (100 μmol/L) or insulin (100 nmol/L) for 5 min, and then AS160 phosphorylation at Thr751, Thr642, Ser588, Ser570, Ser341, Ser318, and total AS160 was measured. E: Primary myotubes were electrically stimulated or treated with insulin (100 nmol/L), or both, for 5 min. The white bar shows insulin stimulation for 5 min and then electrical stimulation, and the black bar shows electrical stimulation first and then insulin stimulation for 5 min. Values represent the mean ± SD. **P < 0.001, *P < 0.01 vs. basal group. ††P < 0.001. Data are from at least three independent experiments.