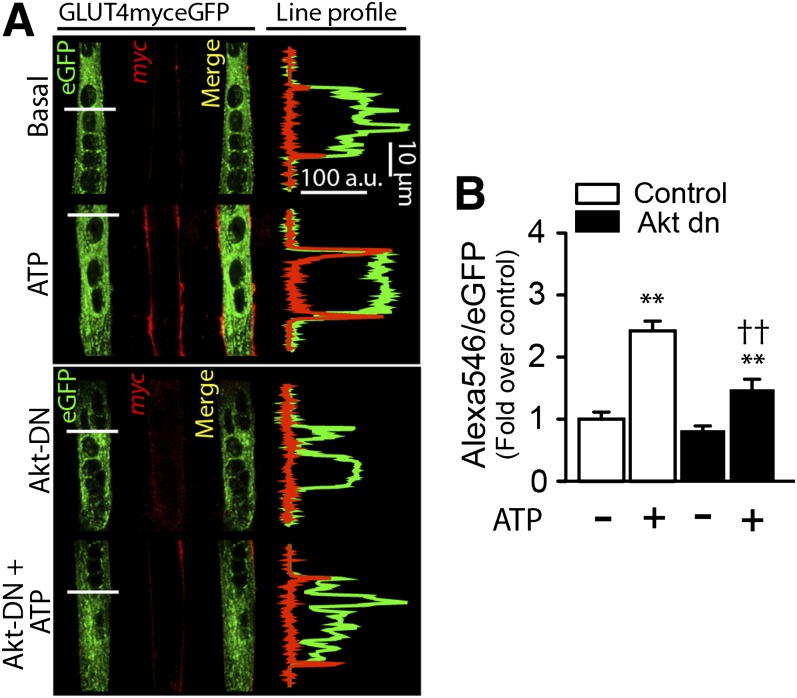
FIG. 4.
ATP-promoted GLUT4myc translocation to the cell surface requires Akt. Primary myotubes were transiently cotransfected with GLUT4myc-eGFP and Akt-dn cDNA for 24 h and then stimulated with 100 μmol/L ATP for 10 min. Extracellular exposure of the myc epitope was detected by immunofluorescence in nonpermeabilized cells as described in research design and methods. Z stack images were collapsed in a single slice (z projection) and results expressed as the ratio of the fluorescence of surface-labeled GLUT4myc (red, Alexa 546) to the fluorescence of total GLUT4 expressed (green GFP). A: Exogenous ATP induced an increase in the Alexa 546-to-eGFP ratio. This ratio was reduced significantly in myotubes cotransfected with GLUT4myc-eGFP and Akt-dn. B: Quantification of panel A. Values are the mean ± SD. **P < 0.001 vs. basal group. ††P < 0.01 relative to ATP stimulation in the control condition. Data are from at least four independent experiments.