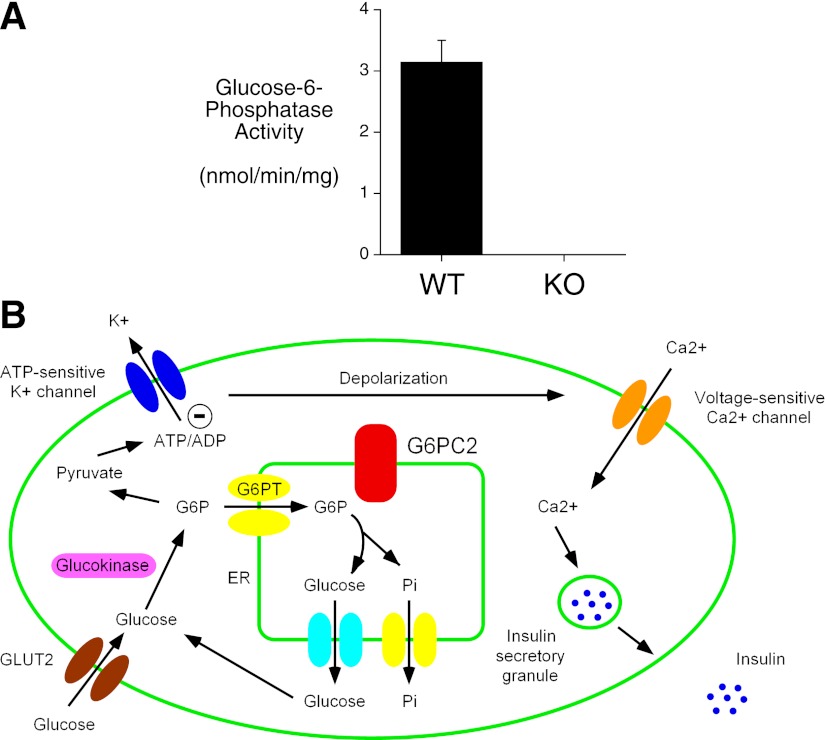
FIG. 1.
G6PC2: a negative regulator of basal GSIS. A: Glucose-6-phosphatase activity was compared in two independent islet preparations isolated from G6pc2 WT and KO mice as described in Research Design and Methods. The results show mean glucose-6-phosphatase activity ± SD. B: A simplified model for GSIS proposing the existence of a glucokinase/G6PC2 futile cycle. The best-characterized pathway for GSIS is shown, although other pathways clearly contribute (40). Overexpression of Gck increases glycolytic flux and results in a leftward shift in the S0.5 for GSIS (31,32). We hypothesize that G6PC2 is a negative regulator of basal GSIS such that a reduction in G6PC2 expression augments glycolytic flux and causes a leftward shift in the dose-response curve for GSIS. The G6P transporter (G6PT) is a G6P–Pi antiporter (41). ER, endoplasmic reticulum.