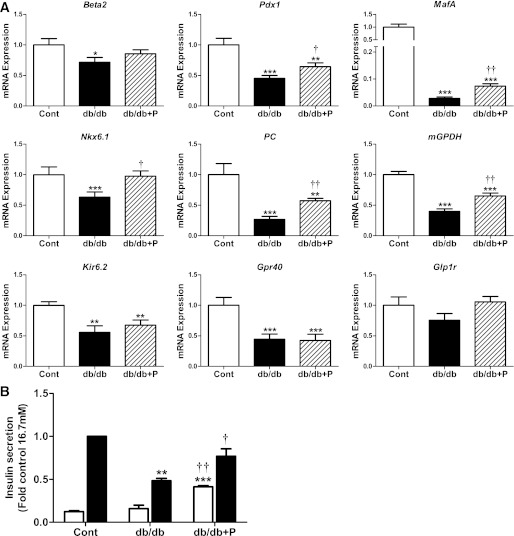
FIG. 6.
Effect of chemical chaperone treatment on the changes in gene expression and insulin secretion in islets of db/db mice. A: Islets isolated from diabetic db/db and age-matched nondiabetic control [cont] mice (12–14 weeks of age) were cultured in the absence (control, white bars; db/db, black bars) or presence (db/db+P, striped bars) of the chemical chaperone PBA (2.5 mmol/L) for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted, reverse-transcribed, and analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. mRNA levels were expressed as fold change of the level in control islets. n = 7 in each group. B: Batches of islets were cultured in Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer containing 0.1% BSA and 2.8 mmol/L (white bars) or 16.7 mmol/L glucose (black bars) for 1 h. Insulin was measured in an aliquot of the buffer by radioimmunoassay. Insulin secretion was expressed as fold change of the level in control islets cultured in 16.7 mmol/L glucose. n = 3 in each group. All results are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 genotype effect; †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01 PBA treatment effect in db/db mouse islets.