Figure 6.
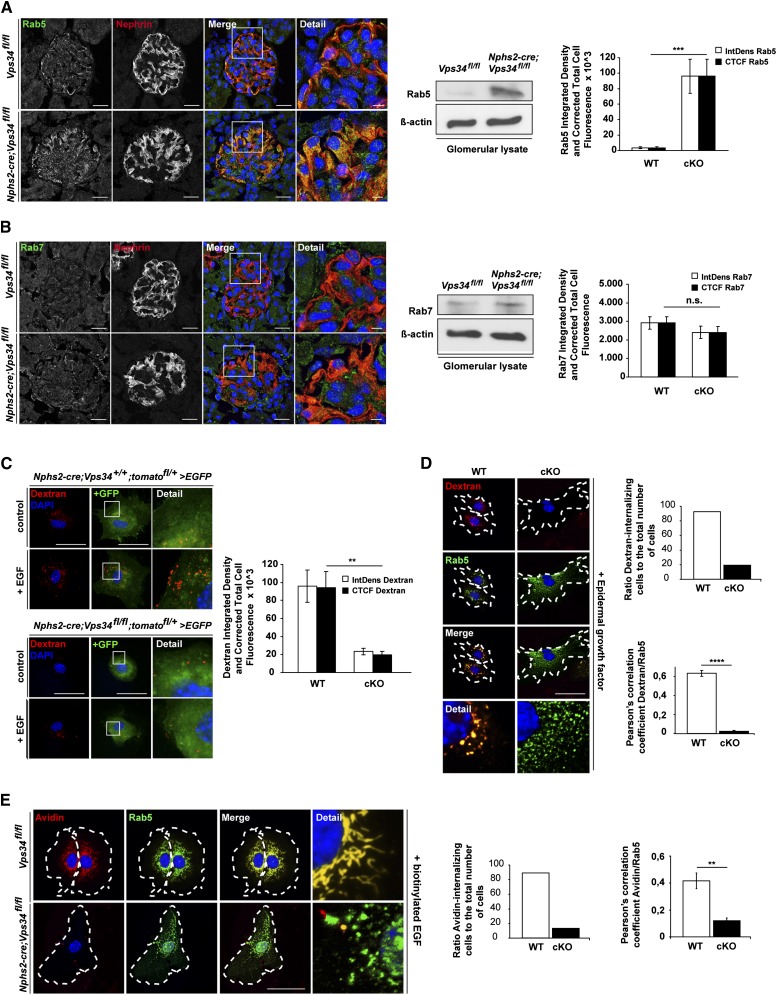
Ablation of Vps34 in mouse podocytes leads to impaired endocytosis. (A and B) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of kidney sections of 3-week-old Nphs2-cre;Vps34fl/fl and littermate control mice. (A) Rab5, a marker for early endosomes and activator of Vps34, was strongly increased in Nphs2-cre;Vps34fl/fl podocytes at 3 weeks of age. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Rab7, a marker for the late endosome, showed no significant differences in podocytes of Nphs2-cre;Vps34fl/fl and Vps34fl/fl mice. Scale bars, 5 µm. (A and B) Western blot analysis of glomerular protein lysates of 3-week-old mice shows that the early endosomal marker Rab5 is accumulated in glomerulus lysates of Nphs2-cre;Vps34fl/fl mice compared with littermate controls. No changes in the late endosomal marker Rab7 can be observed. β-actin was used as loading control. (C and D) Immunofluorescence and quantification of fluid-phase uptake in primary podocytes. Stimulation with 20 nM EGF for 5 minutes induced uptake of dextran in GFP-positive primary control podocytes. In contrast, Vps34-deficient primary GFP-positive podocytes showed impaired uptake of dextran, indicating a blockade in endocytosis. Scale bars, 50 µm. (D) Costaining with Rab5 revealed significant overlap in wild-type podocytes, whereas in Vps34-deficient primary podocytes, Rab5 accumulation did not colocalize with dextran. (E) Immunofluorescence and quantification of streptavidin uptake in primary podocytes. Stimulation of GFP-positive primary wild-type podocytes with 20 nM biotinylated EGF induced uptake of streptavidin coupled to Alexa Fluor 555. In contrast, Vps34-deficient primary GFP-positive podocytes showed impaired uptake of streptavidin, indicating a blockade in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Scale bars, 50 µm. Costaining with Rab5 revealed significant overlap in wild-type podocytes, whereas in Vps34-deficient primary podocytes, Rab5 accumulation did not colocalize with streptavidin. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.