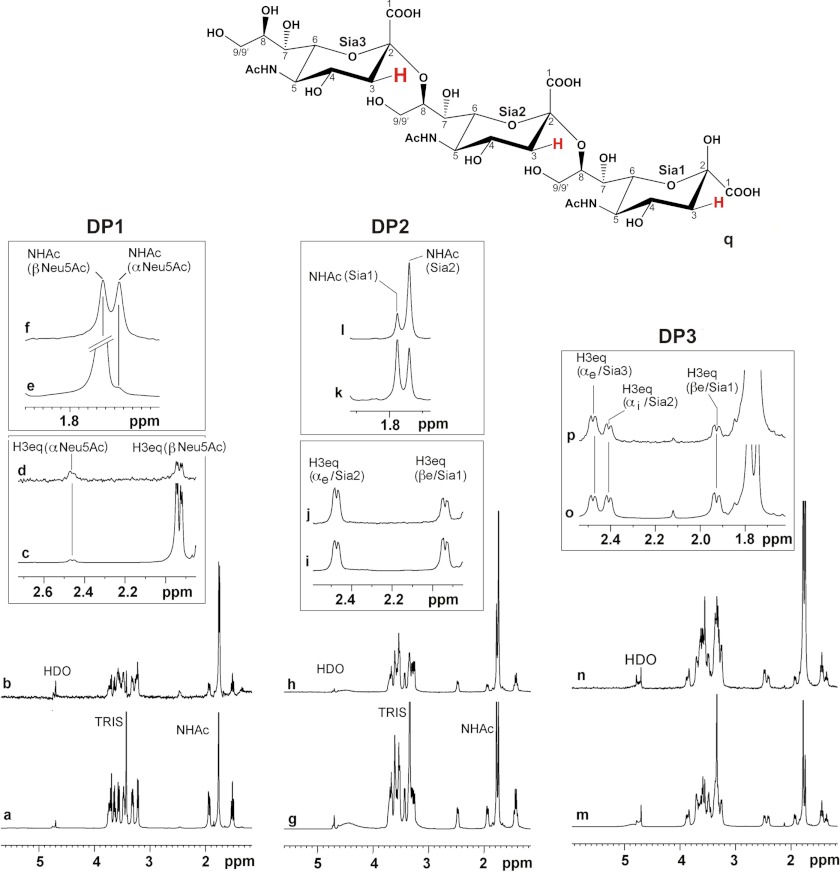
FIGURE 6.
DP1–DP3 are entirely bound by SiaDW-135. 1H and STD NMR were used to study the binding of Sia and oligoSia structures to SiaDW-135. All three compounds (DP1, DP2, and DP3) were entirely bond to the enzyme. However, in the case of DP1 ∼50% of the sugar attained β-configuration (at 1.95 ppm), indicating that the monomer binds to the donor sugar (CMP-Sia) binding site (a–f). In DP2, the dimer of α(2,8)-linked sialic acid residues (g–l), and DP3, the trimer of α(2,8)-linked sialic acid residues (m–p), all sugar units are in contact with the protein. The signals are highlighted for H3eq and N-acetamido protons (NHAc). Although in both compounds the nonreducing end sugar receives the highest energy transfer, only DP3 was found to be an efficient primer to start the enzyme reaction. q, schematic representation of DP3. Differences in saturation transfer are illustrated by the letter size of 3Heq protons. Spectra were recorded at 280 K, 600 MHz using deuterated Tris buffer (20 mm, pH 8.3, and 20 mm MgCl2). Protein resonances were saturated using 40 Gaussian pulses of 5 ms duration at −1.00 ppm. The off-resonance frequency was set to 33 ppm.