FIGURE 8.
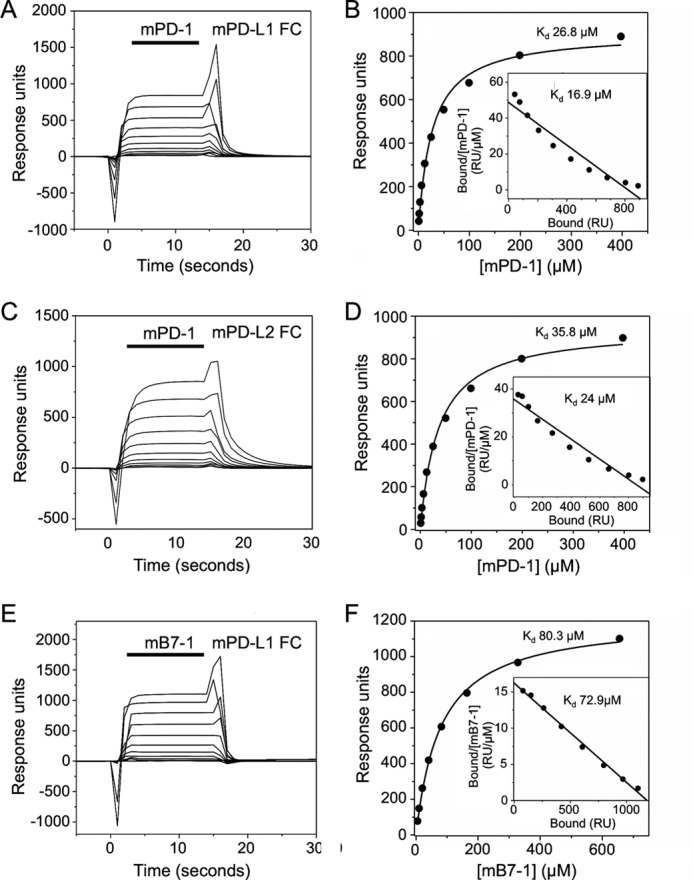
Murine PD-1/PD-L1 interactions (equilibrium binding analyses). A, mPD-1, at a range of concentrations (398 μm and 2-fold dilutions thereof) was injected at 20 μl/min sequentially (solid bar) through a flow cell containing ∼2000 RU of indirectly immobilized mPD-L1 at 37 °C. Background responses observed in a control flow cell containing immobilized hCD4 were subtracted from the total responses to give binding. B, nonlinear curve fitting of the untransformed data using a 1:1 Langmuir binding isotherm yielded a Kd of 26.8 μm and a binding maximum of 908 RU. A Scatchard plot of the mPD-1/mPD-L1 binding data (inset) yielded a Kd of 16.9 μm. C, mPD-1, at a range of concentrations (398 μm and 2-fold dilutions thereof) was injected as in A through a flow cell containing ∼2000 RU of indirectly immobilized mPD-L2 at 37 °C. Background responses have been subtracted. D, nonlinear curve fitting of the untransformed data using a 1:1 Langmuir binding isotherm yielded a Kd of 35.8 μm and a binding maximum of 946 RU. A Scatchard plot of the mPD-1/mPD-L2 binding data (inset) yielded a Kd of 24 μm. E, mB7-1, at a range of concentrations (655 μm and 2-fold dilutions thereof) was injected as in A through a flow cell containing ∼2000 RU of indirectly immobilized mPD-L1 at 37 °C. Background responses have been subtracted. F, nonlinear curve fitting of the untransformed data using a 1:1 Langmuir binding isotherm yielded a Kd of 80.3 μm and a binding maximum of 1215 RU. A Scatchard plot of the mB7-1/mPD-L1 binding data (inset) yielded a similar Kd of 72.9 μm.
