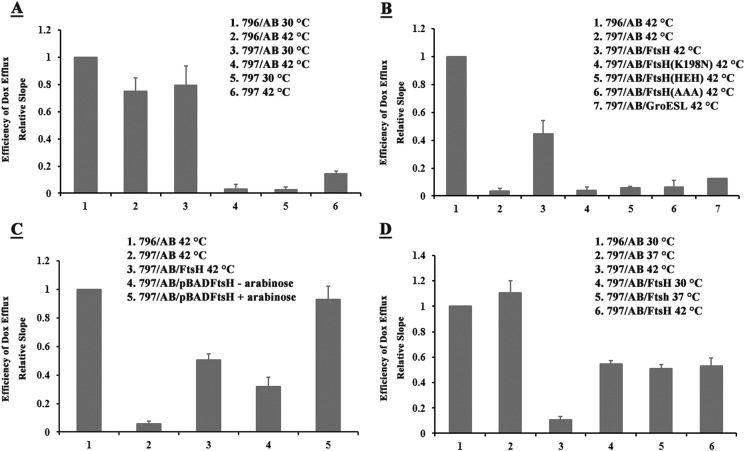
FIGURE 8.
DrrAB-mediated Dox efflux. A, Dox efflux in E. coli 796 or 797 cells. The cells containing pDX101 (DrrAB) or the empty vector were grown at 30 °C to mid-log phase and induced with 0.1 mm IPTG at either 30 or 42 °C for 1 h. The washed cells were loaded with Dox, and efflux was initiated by addition of glucose and detected fluorometrically. The slope of the efflux curve of sample 1 in each panel was designated as 1.0. The efficiency of Dox efflux was then calculated by dividing the slope of each efflux curve by the slope of sample 1. The average data obtained from three independent experiments are shown in the histograms. B, complementation of the DrrAB-mediated Dox efflux in 797 cells by simultaneous overexpression of wild-type FtsH or its variants. E. coli 797 cells containing pDX101(DrrAB) and pUCftsH (wild-type FtsH), pUCftsH(K198N), pUCftsH(HEH), pUCftsH(AAA), or pUCgroESL were analyzed as described under A. C, effect of sequential expression of DrrAB and FtsH on complementation of Dox efflux. E. coli 797 cells containing pDX101(DrrAB) and pBADftsH were grown at 30 °C to mid-log phase and induced with 0.1 mm IPTG for 1 h at 42 °C. The cells were washed extensively to remove IPTG and divided into two halves. One-half was kept at 42 °C for 1 h without any induction (−ara, 42 °C) and the other half was induced by 1% arabinose at 42 °C (+ara, 42 °C) for 1 h. As controls, 796/AB, 797/AB, and 797/AB/pUCftsH were grown at 30 °C to mid-log phase and induced with 0.1 mm IPTG at 42 °C for 2 h. The cells were loaded with Dox, and efflux was measured. The data were analyzed as described under A. D, effect of simultaneous overexpression of FtsH on Dox efflux by DrrAB proteins expressed at different temperatures. 797 cells containing pDX101(DrrAB) and pUCftsH were grown at 30 °C to A0.6, induced with 0.1 mm IPTG at 30, 37, or 42 °C for 1 h, and analyzed as in A.