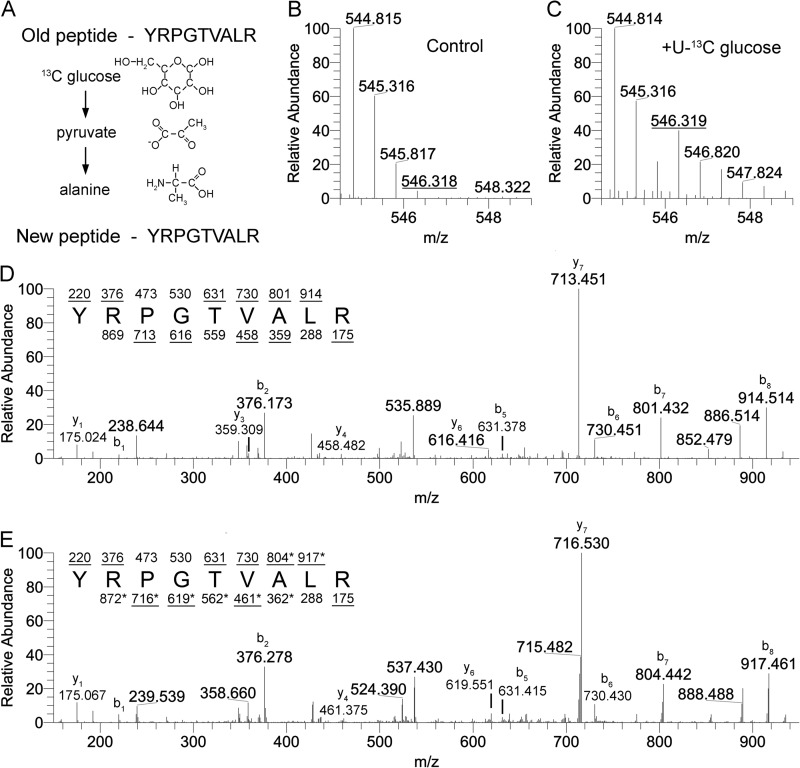
FIGURE 4.
Labeled carbons derived from exogenously provided glucose can be metabolized to form 13C-labeled alanine. A, alanine can be synthesized directly from pyruvate, allowing for labeled carbons from glucose to be incorporated into newly synthesized alanine. Carbons lacking four bonds should be assumed to have hydrogen at those positions. B and C, the 41–49-amino acid peptide from H3 that has no known modification sites shows a shift of a +1.5 m/z species (+3 Da) after 24 h of [13C]glucose treatment. MS/MS analysis of the control peptide treated with unlabeled glucose (D) or [13C]glucose (E) identifies the +1.5 m/z shift as corresponding to alanine based on fragmentation ions. b ions are the fragments starting at the N terminus of the peptide, and y ions are fragments starting on the C terminus of the peptide. Fragments that contain a +3 Da shift are marked with an asterisk. B and C represent [M + 2H]+2 spectra.