FIGURE 8.
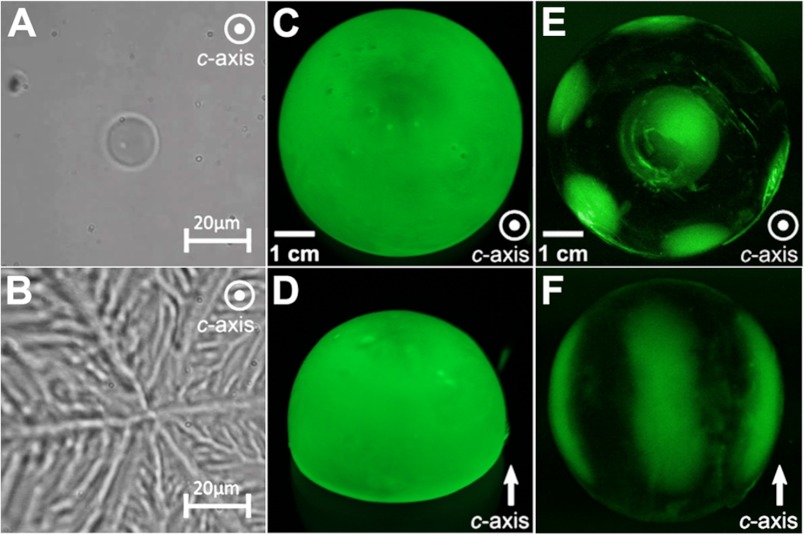
Ice-binding characteristics of RiAFP. A, an ice crystal formed in a solution containing RiAFP has a rounded, oval shape with the c-axis perpendicular to (coming out of) the plane of the page. B, at temperatures below the thermal hysteresis gap, the ice crystal “bursts” laterally along the a-axes in a 6-point dendritic pattern. C and D, top-down and side views of a single ice crystal hemisphere grown in the presence of GFP-RiAFP are shown. The direction of the c-axis is indicated by a white arrow. Green color represents the binding to ice and overgrowth of the GFP-tagged RiAFP, which in this experiment occurs over the entire hemisphere with no indication of preferential ice plane binding. E, an ice hemisphere grown in GFP-LpIBP with its c-axis perpendicular to the page shows binding to the basal plane (center) and six equivalent primary prism planes. F, an ice hemisphere grown in GFP-LpIBP reveals binding to three of the six equivalent primary prism planes, with the other three planes being hidden by the hemisphere. The images in E and F are reprinted with permission from Middleton et al. (38).