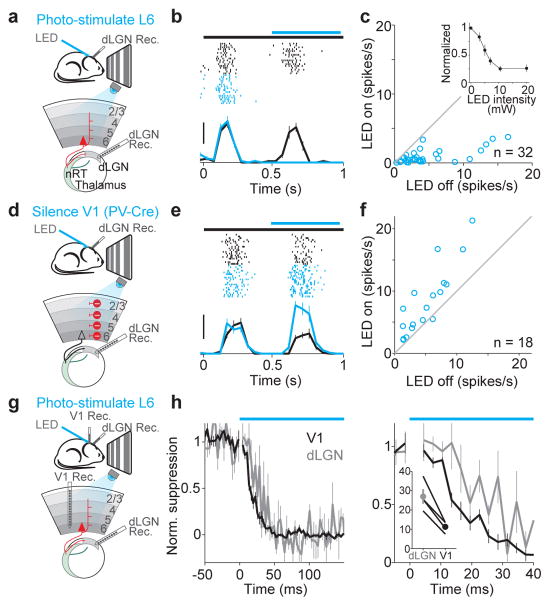
Figure 3. Photo-stimulation of L6 suppresses cortex faster than it suppresses dLGN.
a. Schematic of setup.
b. Visual response of dLGN unit with (blue) and without (black) L6 photo-stimulation Scale bar, 20 spikes/s.
c. Average response of each dLGN unit with and without L6 photo-stimulation. Inset, monotonic suppression of dLGN.
d. Schematic of setup for silencing V1 by photo-stimulation of PV inhibitory neurons.
e. Visual response of dLGN unit with and without photo-silencing of V1. Scale bar, 30 spikes/s
f. Average response of each dLGN unit with and without cortical silencing.
g. Schematic of setup.
h. Left, time-course of L6-mediated suppression of dLGN (gray) and V1 (black) (n = 4). Bin size: 3 ms. Right, same data on expanded timescale. The first bin at LED onset was blanked to remove LED-induced artifact. Inset, time to suppression exceeding 2 SDs from baseline activity in dLGN and V1 (y-axis: ms) for four experiments (p = 0.012).