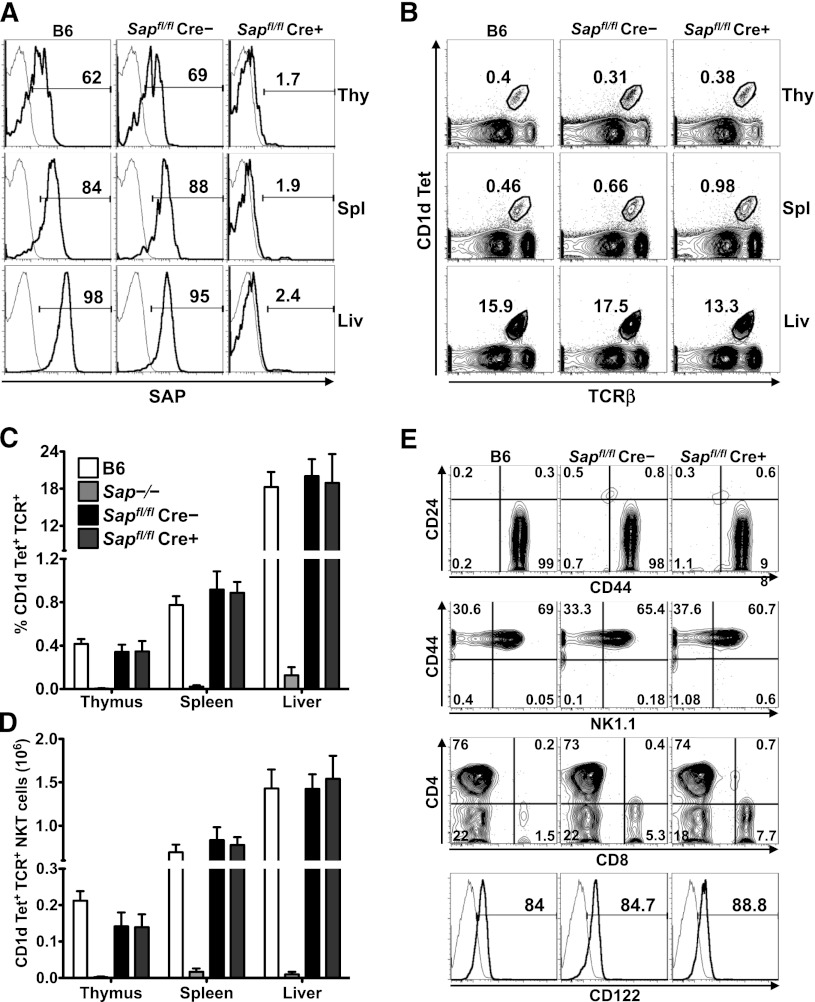
Figure 1.
Conditional Sap deletion leads to loss of SAP expression yet retention of mature iNKT cells. (A) PBS57-CD1d tetramer (Tet)+TCR-β+ iNKT cells from the organs of wild-type (B6) and tamoxifen-treated Sapfl/flCre– and Sapfl/flCre+ mice were stained for intracellular SAP by using an anti-SAP (bold histogram) or isotype control (fine histogram) antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative flow cytometric plots showing the percentages of iNKT cells in the organs of B6 and tamoxifen-treated Sapfl/flCre– or Sapfl/flCre+ mice. Average percentage (C) and absolute number (D) of CD1d-Tet+TCR-β+ iNKT cells in the organs of B6, Sap−/−, and tamoxifen-treated Sapfl/flCre– or Sapfl/flCre+ mice. Data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of 6 animals per genotype. (E) The maturation status of liver iNKT cells was assessed by examining the surface levels of expression of CD24, CD44, NK1.1, CD4, CD8, and CD122. Data in A, B, and E are representative of 6 age-matched mice of each genotype. Liv, liver; Thy, thymus; Spl, spleen.