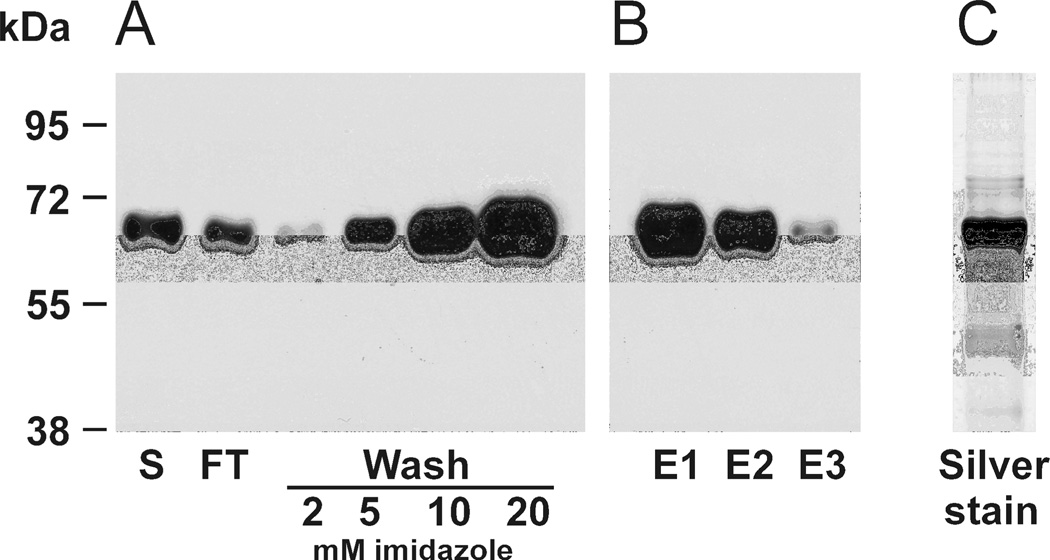
Figure 3. Optimizing the conditions for κGalNAc-T2 isolation using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography.
Recombinant κGalNAc-T2 was expressed in Sf9 cells and purified by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography under native conditions. Binding buffer (1/9 v/v) was added to the cell-culture supernatant (S) and incubated with Ni-NTA agarose (1 ml of 50% slurry per 250 ml) over night at 4°C on roller. The suspension was loaded in a glass column and the flow-through (FT) was collected. Ni-NTA column was washed successively with 10-column volumes of washing buffer with increasing imidazole concentrations (2, 5, 10, and 20 mM). Aliquots corresponding to 5 µl from each fraction were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting with anti-His tag HRP-conjugated antibody. Washing with buffers containing 5, 10, and 20 mM imidazole lead to significant losses of κGalNAc-T2 protein (A). To optimize elution conditions, the purification was optimized, using 2 mM imidazole washing buffer followed by elution with six-column volumes of 200 mM imidazole elution buffer and two-column-volume samples were collected and aliquots corresponding to 5 µl of each fraction were analyzed (E1, E2, and E3); the results showed that four-column volumes (E2) of elution buffer released most κGalNAc-T2 protein (B). Elution fractions E1 – E3 were pooled and concentrated into 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4 to >1 mg protein/ml. Purity of the final κGalNAc-T2 preparation under conditions specified in (B) was assessed by SDS-PAGE analysis of sample corresponding to 1 µl of final κGalNAc-T2 preparation followed by silver staining (C).