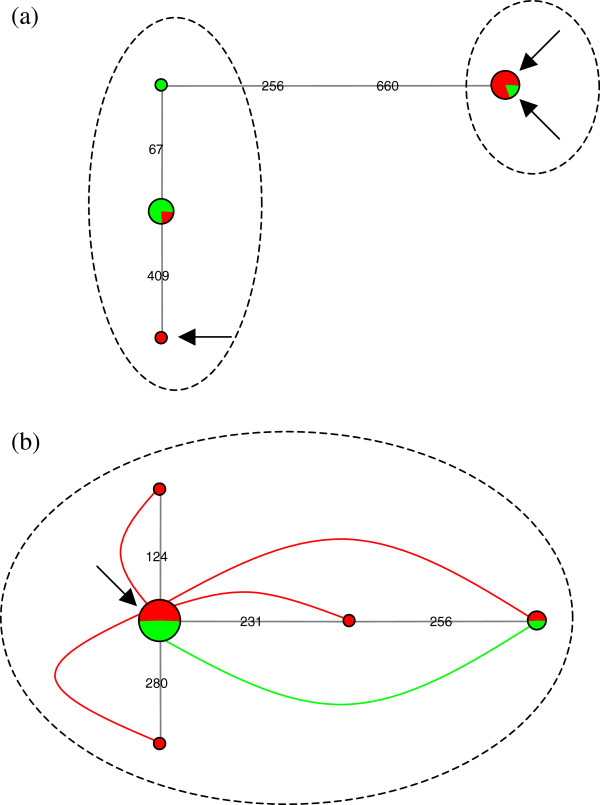
Figure 2.
Phylogeographic analysis of 10 Lophelia pertusa samples from Italy and Norway. (a) Haplotype network (haplonet) of control region (CR) sequences. Green represents Italy and red Norway, whereas the numbers on the lines between haplotypes indicate the position of the corresponding mutations in the alignment (circle sizes are proportional to the number of individuals harboring each haplotype). Dashed ovals delineate two sympatric CR haplogroups (comprising respectively one and three haplotypes). The two arrows in the upper right corner point at the two individuals whose complete mitochondrial genomes were sequenced in the present study, whereas the bottom left arrow shows the CR haplotype in the published sequence of L. pertusa[10]. (b) Haplotype web (haploweb) of ITS2 sequences. The color code is the same as in (a), and curves connecting haplotypes represent heterozygous individuals harboring two different ITS2 types [39]. Circle sizes are proportional to the number of individuals harboring each type. The arrow points at the common ITS2 type shared by all individuals analyzed in the present study as well as by the one sequenced in [10,42], whereas the dashed oval delineates the resulting field for recombination [39,43].