Abstract
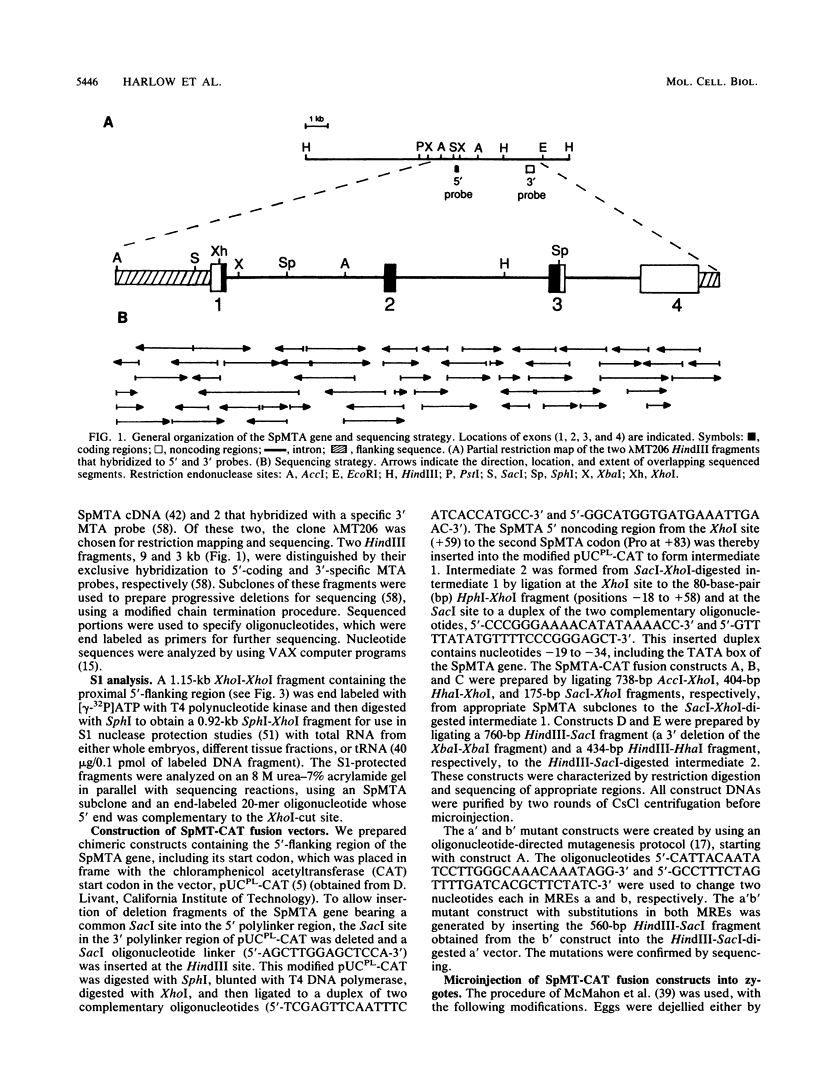
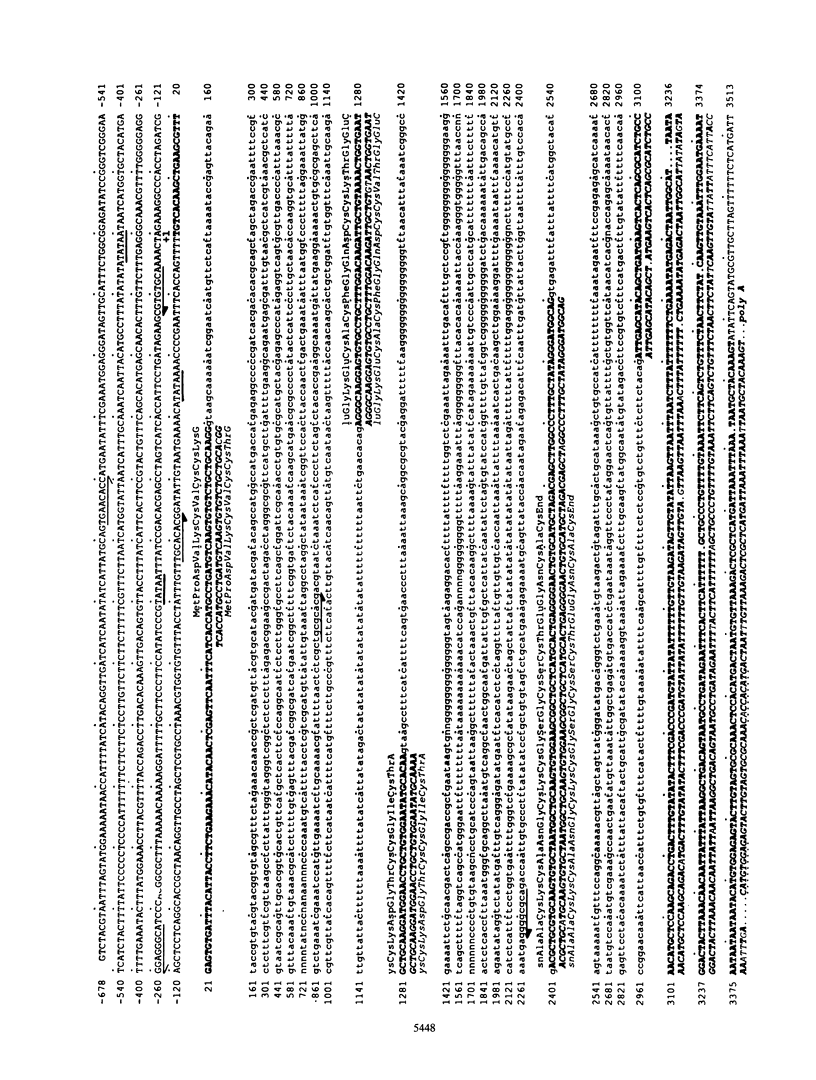
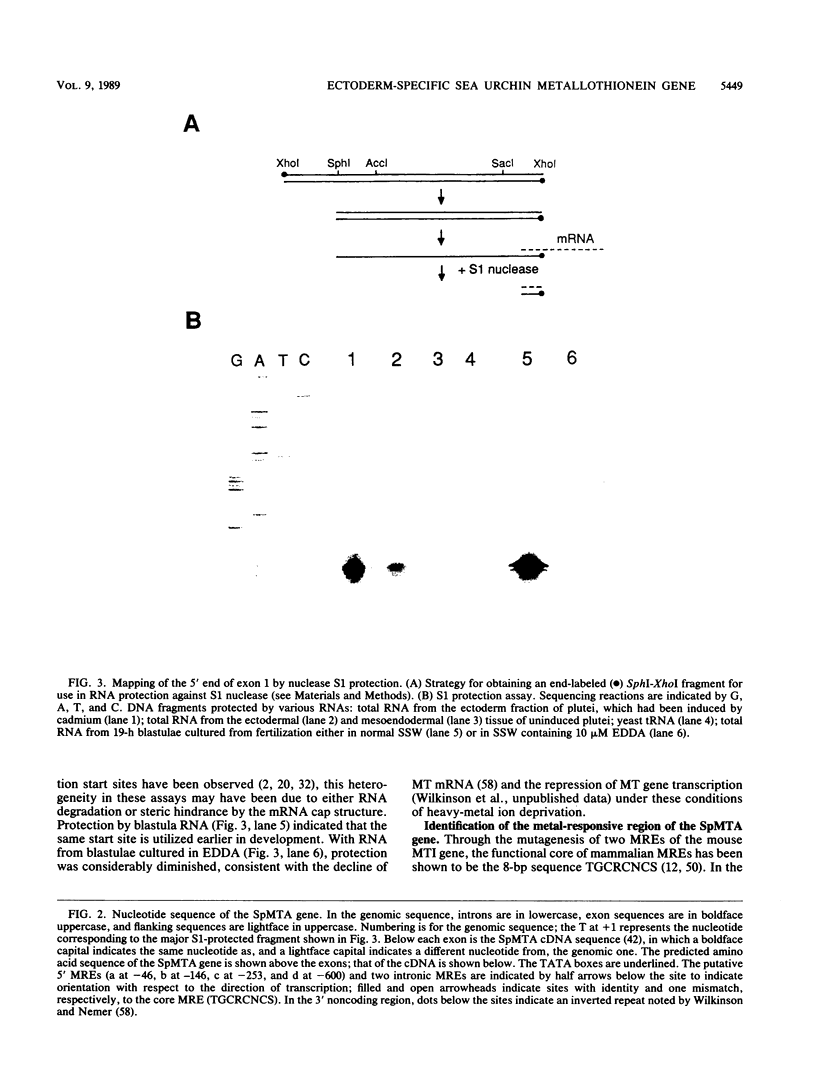
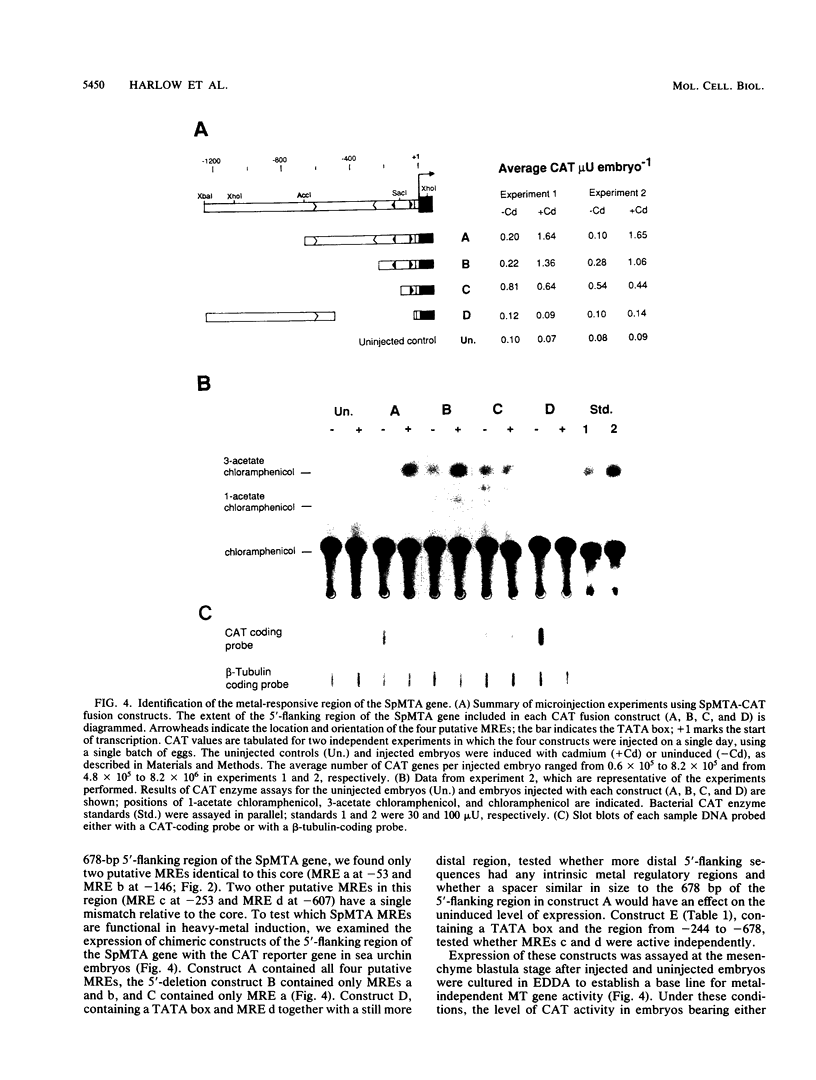
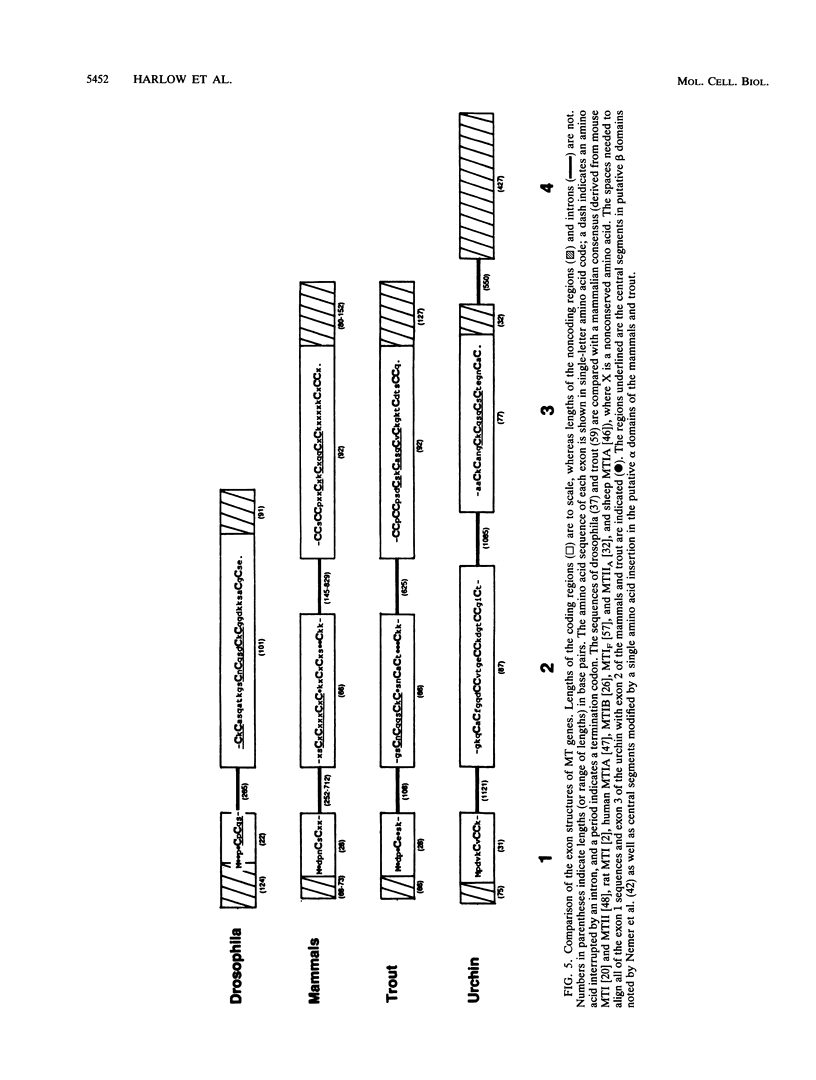
The metallothionein-A gene in the metallothionein gene family of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (SpMTA gene) was sequenced and found to contain three coding exons plus a 3' entirely noncoding exon. Putative alpha and beta MT domains were encoded, by its exons 2 and 3, respectively, in reverse of the order in vertebrate metallothionein genes. The SpMTA promoter was characterized through the expression of recombinant constructs containing various portions of the proximal 678-base-pair (bp) 5'-flanking region of the SpMTA gene. Zygotes injected with constructs were cultured to the blastula stage in the presence of a heavy-metal chelator and then incubated in the presence or absence of cadmium. The longest constructs were expressed only when heavy-metal ion was present. Two putative metal-responsive elements (MREs a and b) within 240 bp of the transcription start site resembled mammalian MREs in their critical 8-bp cores (TGCRCNCS) and in their locations relative to each other and to the TATA box. Elimination of activity by site-specific mutations in MREs a and b, separately or in both, identified them as metal regulatory elements. Thus, MRE recognition in this invertebrate resembles that in vertebrates. Upstream sites with single-mismatched MREs neither acted as MREs nor amplified the activity of MREs a and b. The SpMTA, Spec1, and CyIIIa actin genes, which have the same ectodermal specificity, have common DNA elements at relatively similar locations in their promoter regions; however, these elements are insufficient in themselves to promote gene expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhurst R. J., Calzone F. J., Lee J. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Structure and organization of the CyIII actin gene subfamily of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R. D., Birren B. W., Taplitz S. J., Herschman H. R. Rat metallothionein-1 structural gene and three pseudogenes, one of which contains 5'-regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):302–314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angerer L. M., Kawczynski G., Wilkinson D. G., Nemer M., Angerer R. C. Spatial patterns of metallothionein mRNA expression in the sea urchin embryo. Dev Biol. 1986 Aug;116(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S., Sucov H., Stephens L., Davidson E., Wilt F. A lineage-specific gene encoding a major matrix protein of the sea urchin embryo spicule. I. Authentication of the cloned gene and its developmental expression. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond-Matthews B., Davidson N. Transcription from each of the Drosophila act5C leader exons is driven by a separate functional promoter. Gene. 1988;62(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Cetta A., Davidson E. H. The single-copy DNA sequence polymorphism of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Jones K. C., James T. W. Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Thézé N., Thiebaud P., Hill R. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Developmental appearance of factors that bind specifically to cis-regulatory sequences of a gene expressed in the sea urchin embryo. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1074–1088. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon R. A., Tufaro F., Brandhorst B. P. Post-transcriptional restriction of gene expression in sea urchin interspecies hybrid embryos. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):337–346. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., Angerer L. M., Lee J. J., Davidson E. H., Angerer R. C. Cell lineage-specific programs of expression of multiple actin genes during sea urchin embryogenesis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Mar 20;188(2):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Hamer D. H. Fine mapping of a mouse metallothionein gene metal response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1376–1380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H. Lineage-specific gene expression and the regulative capacities of the sea urchin embryo: a proposed mechanism. Development. 1989 Mar;105(3):421–445. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Herman S. A., Martínez-Salas E., Chalifour L. E., Wirak D. O., Cupo D. Y., Miranda M. Microinjecting DNA into mouse ova to study DNA replication and gene expression and to produce transgenic animals. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):662–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flytzanis C. N., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Ontogenic activation of a fusion gene introduced into sea urchin eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):151–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss K., McClain W. H. Rapid site-specific mutagenesis in plasmids. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks R. R., Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Direct introduction of cloned DNA into the sea urchin zygote nucleus, and fate of injected DNA. Development. 1988 Feb;102(2):287–299. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furey W. F., Robbins A. H., Clancy L. L., Winge D. R., Wang B. C., Stout C. D. Crystal structure of Cd,Zn metallothionein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):704–710. doi: 10.1126/science.3945804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H. Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:913–951. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin S. H., Carpenter C. D., Hardin P. E., Bruskin A. M., Klein W. H. Structure of the Spec1 gene encoding a major calcium-binding protein in the embryonic ectoderm of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow P., Nemer M. Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of beta-tubulin gene expression in the embryo of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):147–160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslinger A., Karin M. Upstream promoter element of the human metallothionein-IIA gene can act like an enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heguy A., West A., Richards R. I., Karin M. Structure and tissue-specific expression of the human metallothionein IB gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2149–2157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinegardner R. Cellular DNA content of the echinodermata. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1974 Oct 15;49(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(74)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Mosaic incorporation and regulated expression of an exogenous gene in the sea urchin embryo. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):198–208. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. T., Boulanger Y., Fesik S. W., Armitage I. M. NMR analysis of the structure and metal sequestering properties of metallothioneins. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Mar;54:135–145. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8454135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Berg P. Effects of the position of the simian virus 40 enhancer on expression of multiple transcription units in a single plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2593–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Dietlin T., Cooke T. Metal-responsive elements act as positive modulators of human metallothionein-IIA enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):606–613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katula K. S., Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Ontogenic expression of a CyI actin fusion gene injected into sea urchin eggs. Development. 1987 Nov;101(3):437–447. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Shott R. J., Rose S. J., 3rd, Thomas T. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sea urchin actin gene subtypes. Gene number, linkage and evolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):149–176. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn D. A., Angerer L. M., Bruskin A. M., Klein W. H., Angerer R. C. Localization of a family of MRNAS in a single cell type and its precursors in sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2656–2660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni G., Otto E., Lastowski-Perry D. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a metallothionein gene of Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Mar;112(3):493–504. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClay D. R., Chambers A. F. Identification of four classes of cell surface antigens appearing at gastrulation in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1978 Mar;63(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Flytzanis C. N., Hough-Evans B. R., Katula K. S., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Introduction of cloned DNA into sea urchin egg cytoplasm: replication and persistence during embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1985 Apr;108(2):420–430. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Travaglini E. C., Rondinelli E., D'Alonzo J. Developmental regulation, induction, and embryonic tissue specificity of sea urchin metallothionein gene expression. Dev Biol. 1984 Apr;102(2):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Wilkinson D. G., Travaglini E. C., Sternberg E. J., Butt T. R. Sea urchin metallothionein sequence: key to an evolutionary diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4992–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson K. B., Winge D. R. Independence of the domains of metallothionein in metal binding. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8698–8701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto E., Allen J. M., Young J. E., Palmiter R. D., Maroni G. A DNA segment controlling metal-regulated expression of the Drosophila melanogaster metallothionein gene Mtn. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1710–1715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Molecular biology of metallothionein gene expression. Experientia Suppl. 1987;52:63–80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6784-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Mercer J. F. Structure and regulation of the sheep metallothionein-Ia gene. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):579–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Heguy A., Karin M. Structural and functional analysis of the human metallothionein-IA gene: differential induction by metal ions and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Davison B. L., Stuart G. W., Wilkie T. M., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation, linkage, and sequence of mouse metallothionein I and II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1221–1230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Stuart G. W., Palmiter R. D. Building a metal-responsive promoter with synthetic regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1480–1489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Stuart G. W., Palmiter R. D. Metal regulatory elements of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Experientia Suppl. 1987;52:407–414. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6784-9_39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Benson S., Robinson J. J., Britten R. J., Wilt F., Davidson E. H. A lineage-specific gene encoding a major matrix protein of the sea urchin embryo spicule. II. Structure of the gene and derived sequence of the protein. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Hough-Evans B. R., Franks R. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. A regulatory domain that directs lineage-specific expression of a skeletal matrix protein gene in the sea urchin embryo. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1238–1250. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J., Hamer D. H. Tandemly duplicated upstream control sequences mediate copper-induced transcription of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae copper-metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1158–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., Jahroudi N., Foster R., Gedamu L. Structure, organization, and regulation of human metallothionein IF gene: differential and cell-type-specific expression in response to heavy metals and glucocorticoids. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):26–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Nemer M. Metallothionein genes MTa and MTb expressed under distinct quantitative and tissue-specific regulation in sea urchin embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):48–58. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafarullah M., Bonham K., Gedamu L. Structure of the rainbow trout metallothionein B gene and characterization of its metal-responsive region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4469–4476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]