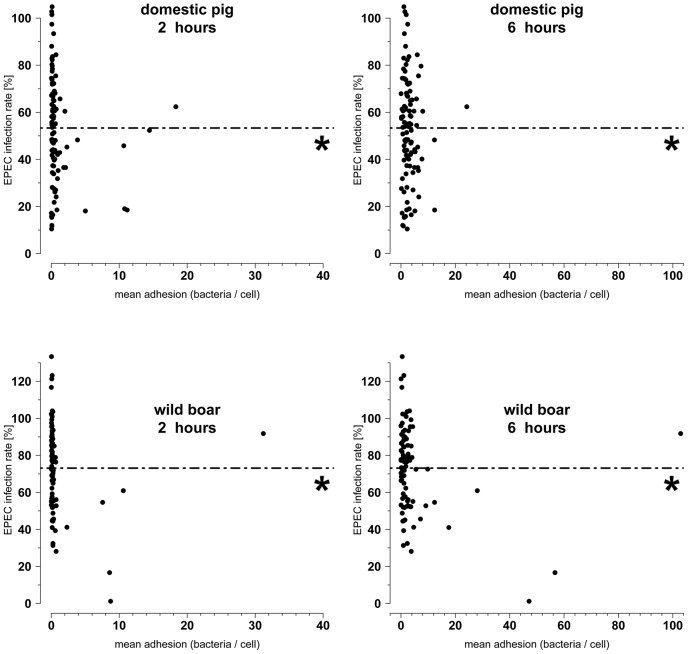
Figure 4. Association of adhesion and a probiotic effect.
X-axis: IPEC-J2 cells were incubated with E. coli over 2 h or 6 h. Adhesion was quantified after removing non-adherent bacteria by washing. Y-axis: EPEC infection rates were determined in an EPEC inhibition assay: E. coli were incubated over 2 h with IPEC-J2 cells. Non-adherent bacteria were removed by washing. Subsequently, IPEC-J2 cells were incubated with EPEC. After 6 h non-adherent bacteria were removed by washing. The EPEC infection rate was calculated in relation to EPEC mono-infection (no domestic pig or wild boar E. coli pre-incubation = 100%). Conclusively, a number below 100% indicates a probiotic effect = reduction of EPEC. Isolates from domestic pigs had a higher probiotic effect ( = higher reduction of the EPEC infection rate (p<0.05)). There were no significant associations between the adhesion capabilities of strains and their probiotic effects. *: Mean of EPEC infection rate.