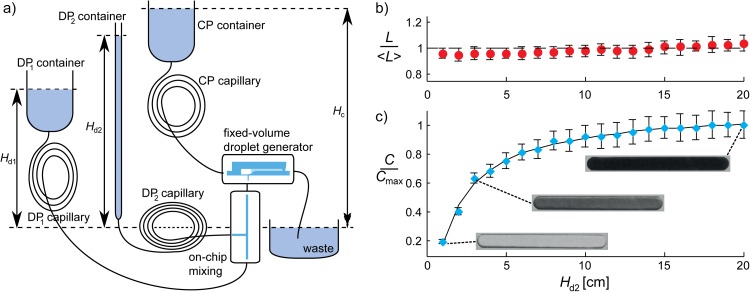
Figure 5.
(a) Setup for the facile generation of monodisperse droplets containing a solute (ink), whose concentration gradually decreases with time, that is, for successive droplets. Prior to emulsification, a concentrated stream of ink () supplied from a tall and narrow container (DP2) is diluted by mixing it on a separate chip with a stream of solvent supplied from a wide container (DP1). The concentration of this mixture, C, continuously decreases due to a decreasing flow rate of the solute stream caused by a decrease in the pressure head . (b), (c) While the length of the droplets is nearly constant (b), the concentration of ink in the droplets (c) depends on according to , with A, B, D, and E constants, as shown from the excellent agreement between the experimental data and the fit (solid line). The error bars indicate the standard deviation obtained by measuring the length and concentration of at least 10 droplets.