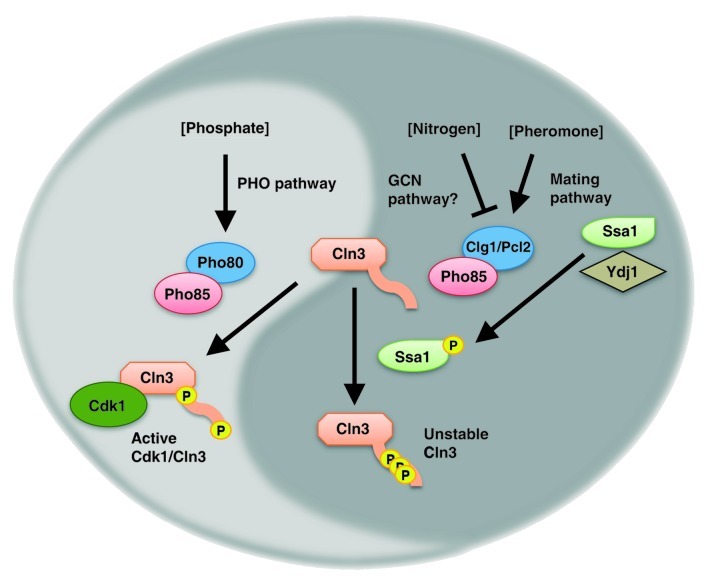
Figure 1. Nutrient signals converge on Cln3 via divergent activities of Pho85. Phosphate availability activates the PHO pathway, wherein the cyclin Pho80 activates the CDK Pho85 to directly phosphorylate Cln3 on the borders of the PEST degron, thereby protecting Cln3 from ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation. The resulting Cln3 stabilization permits Cdk1-Cln3 activity to accumulate and promote G1/S progression. By contrast, nitrogen starvation or sensing of mating pheromone induce cyclins Clg1 or Pcl2 to activate Pho85 to phosphorylate the chaperone Ssa1. Cln3 binding and PEST phosphorylation induce Cln3 degradation. Thus, nitrogen or phosphate starvation similarly block cell cycle progression via regulation of opposing functions of Pho85.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.