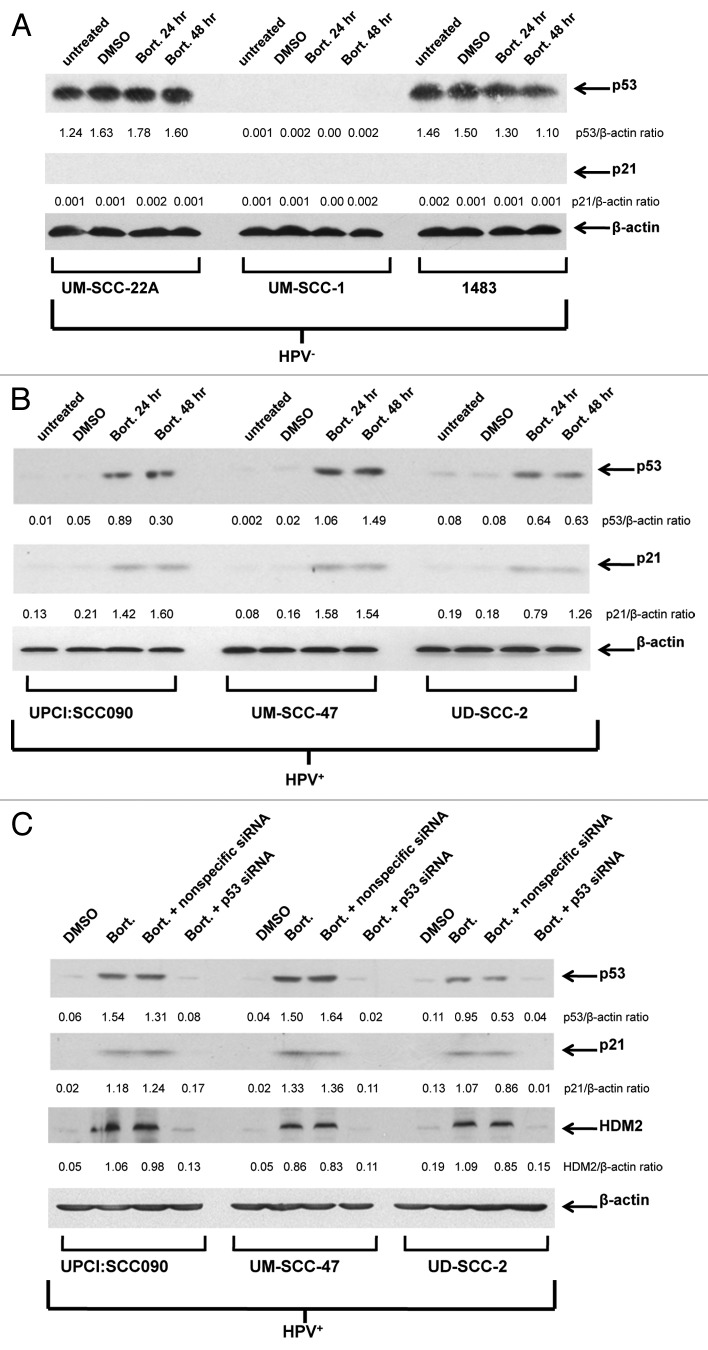
Figure 3. Proteasome inhibition with bortezomib induces functional p53 protein in HPV-positive cells but not HPV-negative cells. Three HPV-negative HNSCC cell lines (A) and three HPV-positive HNSCC cell lines (B) were left untreated, treated for 24 h with 0.1% DMSO, or treated for 24 or 48 h with 50 nM (UM-SCC-22A, UM-SCC-1, 1483, UPCI:SCC090, UM-SCC-47) or 200 nM (UD-SCC-2) bortezomib. Following treatment, immunoblotting was used to detect expression of p53, p21 and β-actin. Ratios of p53/β-actin and p21/β-actin were determined by densitometric scanning. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (C) Suppression of p53 expression/activity in bortezomib-treated HPV-positive cells using p53 siRNA. HPV-positive HNSCC cells were either left untransfected or were transfected with 100 nM nonspecific siRNA or p53 siRNA. After 24 h, untransfected cells were treated with 0.1% DMSO, 50 nM (UPCI:SCC090, UM-SCC-47) or 200 nM (UD-SCC-2) bortezomib, and transfected cells were treated with bortezomib (50 or 200 nM, as above). After 48 h of treatment, immunoblotting was used to detect p53, p21, HDM2 and β-actin. Bortezomib induction of p53 and the products of p53 target genes were inhibited by p53 siRNA, but not nonspecific siRNA. The experiment was performed three times with similar results.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.