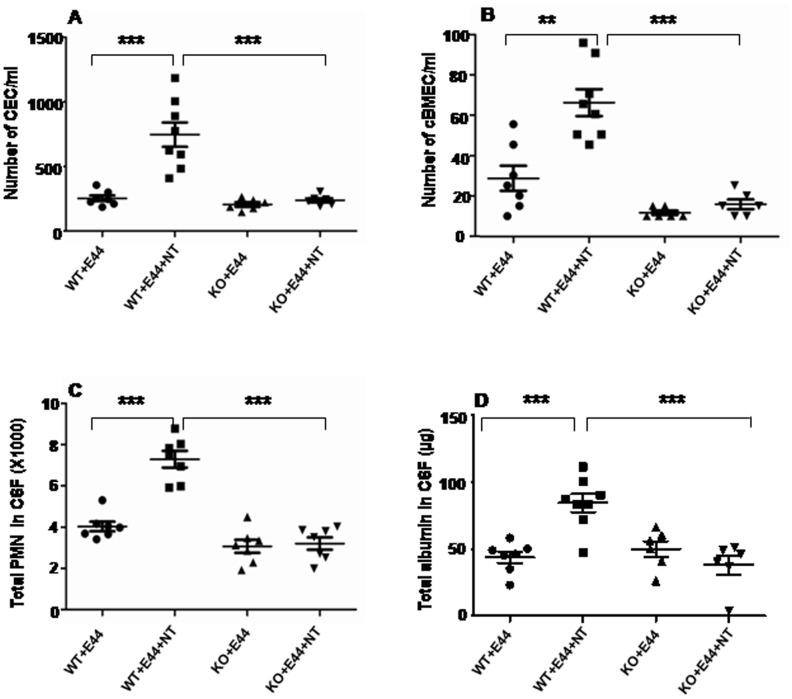
Figure 5. Effects of genetic blockage of α7 nAChR on nicotine-increased BBB permeability and E44 transcytosis.
Triple staining (TS) of murine cBMECs isolated by the use of magnetic beads coupled with UEA-I, which specifically binds to EC [35]. CEC and cBMECs were isolated from wildtype (WT) and α7 deficient (KO) murine pups treated with nicotine (NT), E44 or NT plus E44. Cells without treatment were used as a control. TS was done by DAPI (blue)/antibodies against CD146 (FITC/green) (A: CEC) and S100B (for brain) (rhodamine/red) (B: cBMECs, CD146+/S100B+/DAPI+) or CD133 [for Progenitor ECs(PEC)/rhodamine/red] (PEC: CD146+/CD133+/DAPI+)(Figure S1). CECs and cBMECs were counted with six random fields. (*P<.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001). CNS inflammation and BBB injury were further confirmed by quantification of PMN (C) and albumin (D) in CSF, which have been extensively used for assessing BBB disruption [31].