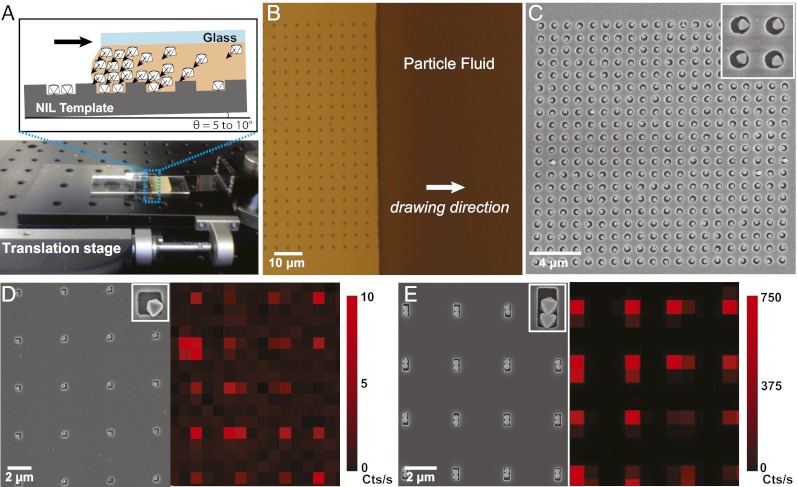
Fig. 4.
Oriented assembly of polyhedral plasmonic nanoparticle clusters using gravity-driven nanoparticle printing. (A) Scheme and photo of the assembly setup that was used in an environment with minimal air currents. A solution of particles in DMF is sandwiched between fixed glass coverslip and an NIL template on a single-axis translation stage. The setup is tilted to 5–10°, causing the particles to accumulate at the air/solvent/substrate interface. Once the dense particle fluid has formed, the stage is used to move the NIL template, drawing the nanoparticle fluid across the pattern (B). The high concentration of particles at the interface forces particles inside the recessed pattern, which are left behind once the particle fluid crosses the pattern (C). SEM images and corresponding SERS intensity maps of patterned single octahedra and dimers using 633-nm excitation and monitoring the 1079 cm-1 band of 4-AMT (D and E). Measurements are reported in counts/second. For SERS measurements, particles were assembled in pits spaced 4 μm to ensure each measurement corresponded to a single particle or assembly.