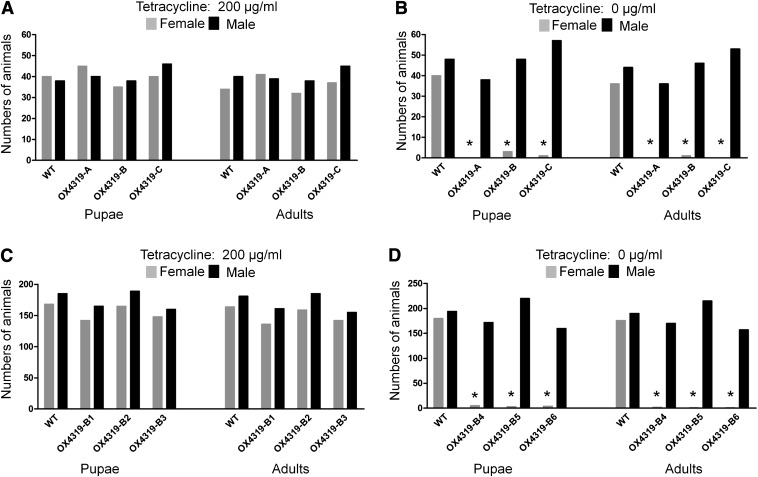
Fig. 3.
Repressible female-specific lethality in transgenic silkworms. Newly hatched first-instar transgenic (fluorescent) and WT larvae were reared on a diet with (A and C) or without (B and D) 200 μg/mL tetracycline. These larvae were either heterozygous G2 larvae from each of three independent lines OX4319-A, OX4319-B, and OX4319-C (A and B) or G4 homozygotes (C and D) derived from OX4319-B (six batches OX4319B1-6). Survival of these larvae to pupae and adults was analyzed. Neither heterozygous nor homozygous transgenic lines showed large deviation in sex ratio from WT when reared on diet with tetracycline (A and C), but very few transgenic females survived when reared on diet without tetracycline (B and D). Significant female-specific lethality is marked with asterisk (χ2 test, P < 0.01).