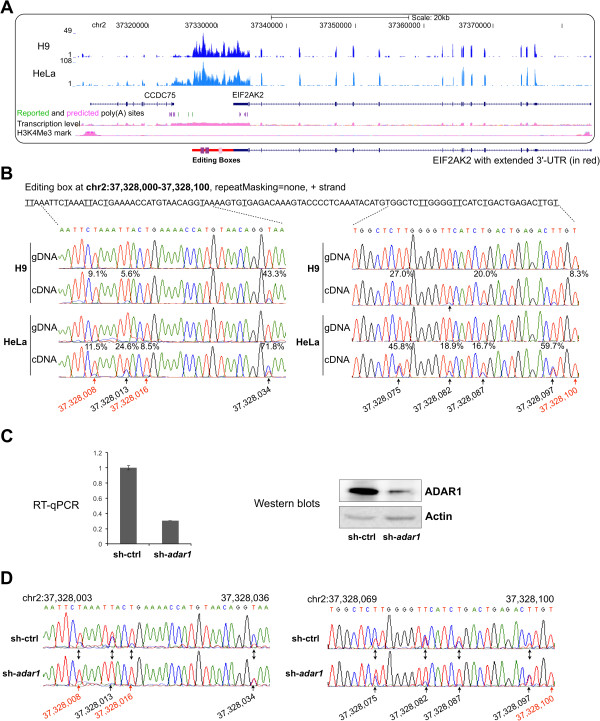
Figure 5.
Validation of constitutive A-to-I sites in non-repetitive editing boxes. (A) Three editing boxes were identified within an intergenic region at chromosome 2. A screenshot from the UCSC genome browser for its sequencing signals in H9 cell (dark blue) and HeLa cell (light blue) with annotated gene models (exons in thick dark blue bars, introns labeled with arrowheads as transcription direction) was shown. CCDC75 is transcribed from the plus strand while EIF2AK2 is transcribed from the minus strand of chromosome. A new gene model of EIF2AK2 with extended 3′ UTR (red line) is drawn beneath the UCSC genome browser snapshot box. Two editing boxes in non-repetitive regions (purple bars) are located in the extended 3′ UTR region together with another editing box in Alu (pink bar). (B) Validation of constitutive A-to-I editing sites. Predicted A-to-I editing sites were indicated with underlines (shown as T-to-Cs on plus strand of chr2), and their predicted editing ratios were shown above each site in the cDNA sequencing chromatograms. Novel editing sites were highlighted with red arrows and their genomic sites were indicated in the bottom, reported sites were in black. (C) Knocking down of adar1 in HeLa cells with shRNA. Both RT-qPCR (left panel) and Western blots (right panel) showed a successful ADAR1 knockdown (sh-adar1) compared with a scramble shRNA (sh-ctrl). (D) Newly identified promiscuous A-to-I editing sites in non-Alu elements are catalyzed by ADAR1.