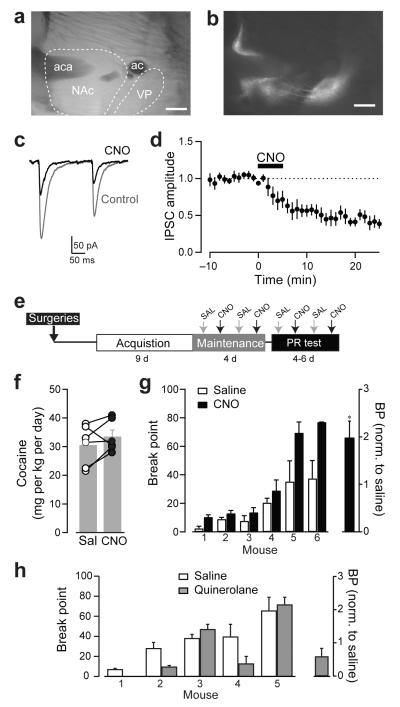
Figure 4. Inhibition of indirect-pathway D2-MSNs increases motivation for cocaine.
(a) Bright field image of sagittal section and (b) fluorescence image showing DREADD expression in NAc neurons and projections to ventral pallidum. aca, anterior commisure ant; ac, anterior commisure. Scale bars = 500 μm. (c) Representative traces of ChR2-evoked IPSC recorded in ventral pallidum neurons before (grey) and after CNO (10 μM) application. (d) Time course of the CNO inhibition of IPSC amplitude in ventral pallidum neurons (n = 7). (e) A diagram describing the experimental timeline. (f) Cocaine intake for animals receiving saline (open) or CNO (solid). (g) Left, Breakpoint values achieved by individual mouse during 4-6 consecutive progressive ratio sessions (PR test) in which mice randomly received saline (open) or CNO (solid, 1 mg/kg). Inset, BP values after CNO normalized to individual saline values (h) BP values achieved by individual mouse during 4 consecutive progressive ratio sessions (PR test) in which mice randomly received saline (open) or D2 agonist quinelorane (gray, 0.03 mg/kg). Inset, BP after quinelorane normalized to individual saline values. *p < 0.05, paired t-test (f) and one sample t-test (g, h). Data are mean ± SEM.