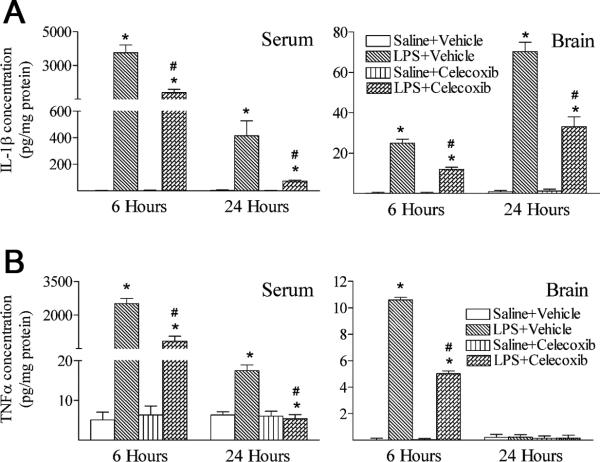
Fig. 4.
Celecoxib attenuated systemic LPS-stimulated increases in inflammatory cytokines (A, IL-1β and B, TNFα) in the rat brain 6 hours or 24 hours after LPS injection. A, IL-1β and B, TNFα concentrations were determined by ELISA kit and presented in the unit of pg/mg protein, as described in Methods. Six hours following LPS injection, serum and brain levels of IL-1β (A) and TNFα (B) were elevated as compared with the Saline + Vehicle group. Twenty-four hours following LPS injection, serum levels of IL-1β (A) and TNFα (B) were still elevated as compared with the Saline + Vehicle group. The concentration of TNFα in the rat brain returned to the control level 24 hours after the LPS exposure (right panel of B), but IL-1β concentration in the LPS-exposed rat brain remained increased as compare with that in the control rat brain (right panel of A). Treatment with celecoxib attenuated induction of IL-1β and TNFα contents by LPS. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of six animals in each group, and analyzed by oneway ANOVA. * P < 0.05 represents a significant difference for the LPS + Vehicle group or LPS + Celecoxib group as compared with the Saline+Vehicle group. # P < 0.05 represents a significant difference for the LPS + Celecoxib group as compared with the LPS + Vehicle group.