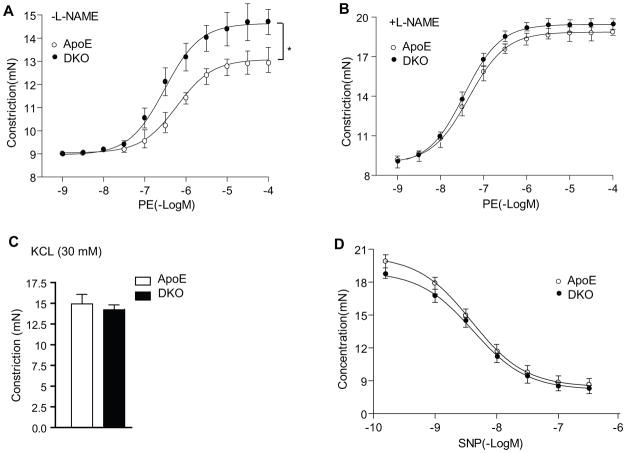
Figure 6. AIP1 deletion augments EC dysfunction at early phases of atherosclerosis.
ApoE−/− and DKO adult mice were fed with Western-type diet for 2 weeks, and aortas were harvested for vessel function assays. A. Aortic rings were contracted with PE at a full range of doses (10−9-10−4 M). Constriction force (mN) is shown. B. Aortic rings were incubated with a NOS inhibitor L-NAME (100 μM) to remove basal NO synthesis and then contracted with PE as in A. C. AIP1 deletion has no effects on vessel constriction in response to KCl. Aortic rings were contracted with 50 mM of KCl. D. AIP1 deletion has no effects on vessel relaxation to the NO donor drug SNP. Aortic rings were incubated with a NOS inhibitor L-NAME to remove basal NO synthesis followed by a precontraction with PE as in A, and were then relaxed with SNP at a full range of doses (10−9-10−6 M). Data in A–D are presented are mean±SEM, with n=5 animals and eight aortic rings per animal, *, p<0.05 indicate that statistically significant by comparing DKO versus ApoE−/−.