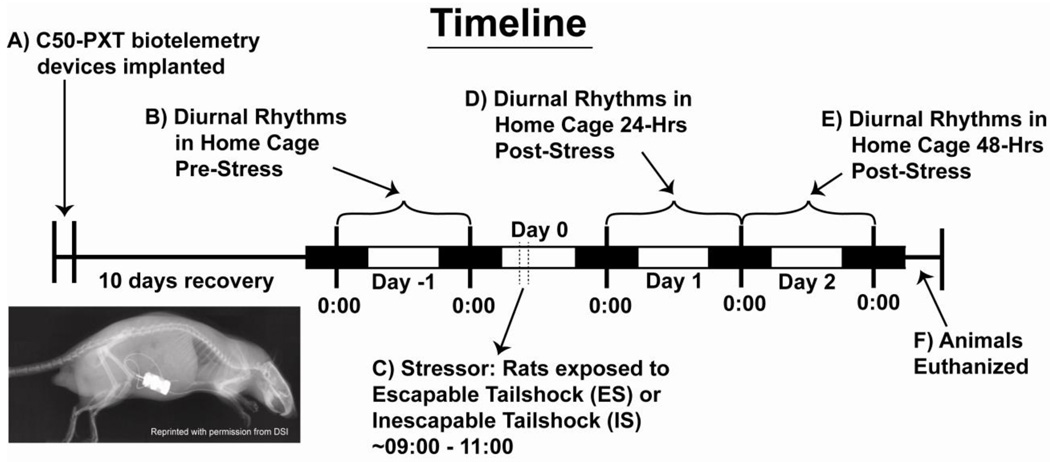
Figure 1.
A) Rats were implanted with the C50-PXT biotelemetry devices and allowed 10 days to recover before recording began. B) Diurnal rhythms were measured uninterrupted in the home cage for twenty-four hours from midnight to midnight (Day -1) before stressor exposure. C) The following day (Day 0) rats were exposed to either escapable stress (ES) or yoked inescapable stress (IS). Diurnal rhythms were again measured uninterrupted in the home cage for D) twenty-four hours (Day 1) and E) forty-eight hours (Day 2) from midnight to midnight.