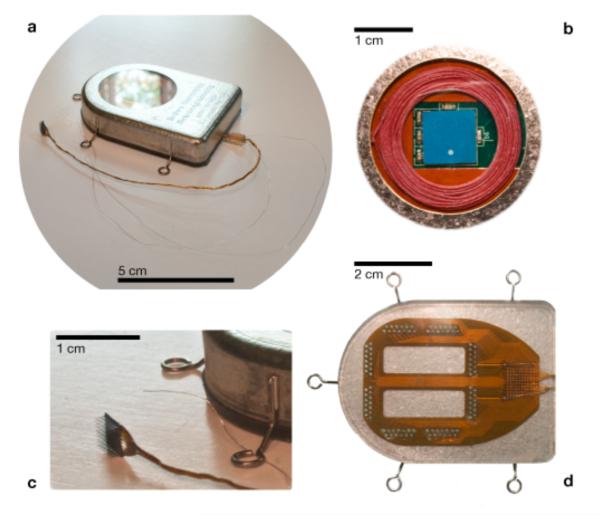
Figure 2.
A wireless neural interface, hermetically sealed, for untethered neuroscience and clinical use. An image of the device after hermetic closure (a) and ready for implant. In a view through the single crystal sapphire window (b), used for electromagnetic transparency, the receiving power coil (red) and the wide band data telemetry chip antenna (blue) can be seen. The intracortical neurosensor, manufactured at Blackrock Microsystems (c), and a reference wire can be seen in relation to the subcutaneous enclosure. Individual wires enter the enclosure through Pt/Ir and ceramic feedthroughs from a flexible polymer (d) interconnect board sealed to the bottom (outside) of the titanium enclosure. The interconnect board is packaged in biocompatible silicone rubber to maintain robust electrical isolation of the input electrodes.